本文是一篇行政管理毕业论文,这项研究深入分析了这两个主题中的每一个,并在两者并列的基础上继续采用整体方法。第三章和第四章阐述了两个项目的前提,并从各自的角度解释了它们是如何相互影响的。《“一带一路”倡议》(一个由一个国家提出的项目,在全球范围内产生影响,特别关注基础设施部门,见第三章)和《巴黎协定》(巴黎协定)的具体特点导致有必要一起分析它们。
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Research Purpose
1.1.1 Note on originality
The following quote by Dennis Weaver sums up the motivation behind choosing this topic: “We don’t have to sacrifice a strong economy for a healthy environment”. It can be argued that in the new technological era, it might actually make it stronger.
Focusing on a compelling research, that covers all the aspects of interest in the area proposed for analysis, the current paper underlines a series of novelty factors. An important first distinction is found in the two sides of the research that will merge to answer to the proposed questions. From the Belt and Road Initiative point of view, we can definitely say it is the only international project of this magnitude. Even more interesting are the international implication of Belt and Road Initiative and its vast planned expansion. From ‘The Paris Agreement” perspective we are facing a bindery agreement that aims to produce a series of significant effects.
Looking at two new approaches in terms of international project development and transboundary environmental protection, the impact of each of them is highly projected onto the other one. The novelty of the research lies in seeing the two concepts side by side and looking into their convergence.
1.2 Research Background
1.2.1 Research background
About the research background, it should be stated, that while there are some specific papers written strictly about the Belt and Road Initiative and `The Paris Agreement`, in order to properly cover the proposed research topic, the focus had to fall on what has been written before the decisions were made. From China`s ascension – reaching such an incredible economic growth and its subsequent need to improve existing infrastructure and to globally expand it, therefore proposing a project like `Belt and Road Initiative`, to how the world countries came about to understand the need to prevent the alarming climate change and how does `The Paris Agreement` proposes to support the process, there are countless approaches and perspectives to look into these subjects.
It is important to analyze and properly explain how the two topics brought into discussion are fundamentally different concepts. On one hand, we are talking about a public policy of global magnitude - `The Paris Agreement`; on the other hand, we are looking into a global project, mainly focused on a transboundary infrastructure construction (though the other aspects should not be ignored, such as: international collaboration, international investments, new emerging international entities who act as International Organizations and many more).
Firstly, in order to understand the origins of the two key concepts of the paper, studies that show how they came about have to be taken into account. In the case of `The Paris Agreement`: it can be the United Nation reports and subsequent decisions on combating the effects of climate change; it can also be about the distinction of using the format of an international non-binding agreement, rather than a binding international treaty, but making it binding by its finality; or the Millennium Development Goals that can stand in for the importance and herculean work behind the adoption of `The Paris Agreement` as part of goal number seven `ensure environmental sustainability`[65]. While for the Belt and Road Initiative the research starts from information about Silk Road, as well as factors that led China to such point in history, where it could financially, politically, logistically to propose such an Initiative.
CHAPTER 2 THEORETIC AND ACADEMIC CONTEXT
2.1 Definitions
Both subjects discussed in the paper are relatively new (compared with topics such as economy, management, engineering, international law). This leads to the need to explain the topics from an academic point of view, stating with what they mean, how they operate, what it involves and so on. Furthermore, both the Belt and Road Initiative and `The Paris Agreement` involve a series of particularities, as well as addressing many classic domains, such as those up mentioned (economy, management, engineering, international law). For this reason it is required a short presentation of each topic, with an extent explanation of their particularities (for example: while there are many infrastructure projects around the world, some at a huge scale, not many are transboundary infrastructure projects – passing from country to country, which leads to a series of important particularities).
2.1.1 Definition of the main terms
a) One Belt One Road Initiative
While on two official visits, back in 2013, in Astana, Kazakhstan[23] (at the Nazarbayev University) and in Jakarta, Indonesia[24] (at the Parliamentary gathering) the President of People`s Republic of China, Xi Jinping, presented the idea of the One Belt One Road Initiative. The name was later officially changed to what is now known as the `Belt and Road Initiative`, it can be described as a global strategy for infrastructure development in around 70 countries (the number is different depending on the source) adopted in 2013 by the Chinese government. One of the sources says that the Initiative “involves more than 100 countries and over 60% of the world's population”, the authors naming it a “magnificent, yet experimental initiative”.
2.2 Conceptual framework
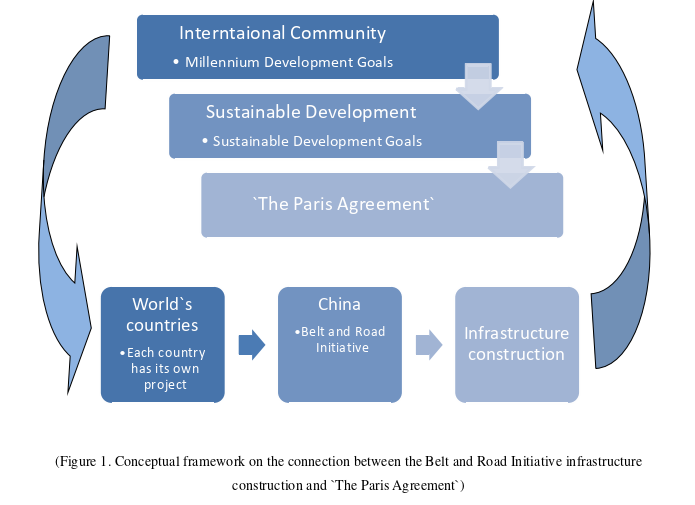
The next paragraphs focus strictly on the conceptual framework in order to paint a comprehensive understanding over the linkage between the key concepts of the research. The graphic below tries to visually explain the theoretic part.
The world`s experts gathered in a series of general meetings and some specific ones and reached an agreement that the current state of the world it is not where it should be in accordance with its full potential. They have agreed upon a series of public policies with global effect, starting from the Millennium Development Goals (MDG/MDGs).[65] At its core, the eight goals of the MDG require economic growth and environmental protection, under a larger spectrum. Afterwards, the Sustainable Development concept was elaborated and expanded on as a need to express that both major goals have to be achieved at the same time and not one on the expense of the other. In order to see the goals achieved, the international community (countries officials, experts, politicians, theoreticians, scientists) developed a framework, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG/SDGs),[63] to keep track of the development, as well as use it as a reminder of the major, universal goal. Based on all this, and probably influenced by the new trend of conducting the international relations, the result was the adopting of `The Paris Agreement`.
第三章“一带一路”基础设施建设分析 ………………………27
3.1.“一带一路”倡议 ………………………………30
3.1.1.历史与地理 …………………30
3.1.2.从丝绸之路向“一带一路”转型 …………………31
第四章“巴黎协定”的特殊性分析 ………………………………41
4.1.一般介绍 ………………………………41
4.2.国际法特殊性 ……………………47
第五章两个主要概念之间联系的讨论 …………………………58
5.1.“一带一路”倡议与《巴黎协定》的相关性 …………………………59
5.1.1.特殊链接 ………………………………59
5.1.2目标评估……………………………61
CHAPTER 5 DISCUSSION ON THE CONNECTION BETWEEN THE TWO MAIN CONCEPTS
5.1 Correlation between Belt and Road and `The Paris Agreement`
5.1.1 Special links
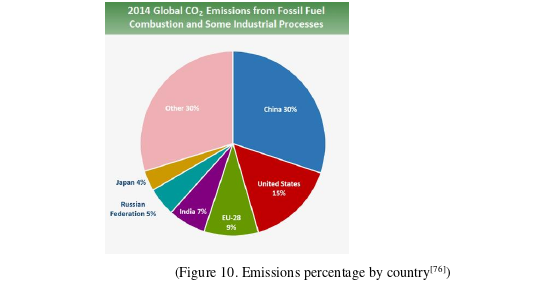
Countries started submitting their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) after `The Paris Agreement` was ratified by enough parties. Belt and Road Initiative, as China’s first transboundary economic and development infrastructure project, covers more than 70 countries. The combined primary energy use of the states across Belt and Road Initiative, account for 50.8% of the global energy consumption. Whether or not the countries involved in the Belt and Road Initiative can successfully implement their NDCs “will be critical to the global efforts to achieve the 2 and 1.5 degree goals”.
The international community remains cautious towards Belt and Road Initiative due to the concerns that China`s goal is to move the outdated and excess industry abroad in order to focus on the new, innovative technology, without losing the economic value of the first ones. There are also concerns regarding the wide scale of the Initiative and the covered targeted region, which is considered environmentally-fragile. Another contingency point comes from the potential environmental impacts of investments in countries with inefficient environmental laws and unstable governance. In order to assuage these concerns, China has been using various dialogue platforms, both domestic and international, to reaffirm its goal of aiming towards a “green, healthy, intelligent, and peaceful” Belt and Road. Furthermore, the cooperation mechanisms set in place show China`s intention to work alongside the international community to meet the Sustainable Development Goals. President Xi Jinping also declared that “taking a driving seat in international cooperation to respond to climate change, China has become an important participant, contributor, and torchbearer in the global endeavor for ecological civilization”.
CONCLUSION
The present Master`s thesis focuses on a delicate, complex, mainly theoretic and slightly controversial topic. “`The Paris Agreement`: Ally or Impediment for the Belt and Road Infrastructure Construction” brings into discussion two smilingly contradictory subjects which are expected to have a major universal impact. This paper brings together, in an interdisciplinary theoretical research, a global wide infrastructure development project, Belt and Road Initiative, a flagship programme of the People`s Republic of China and a transboundary environmental protection document, `The Paris Agreement`, a flagship programme of the United Nations.
The research analyzes in depth each of the two topics, individually and continues with a holistic approach over the juxtaposition of the two. The third and forth chapters set the premises for the two projects, as well as explaining from their respective perspectives how they influence each other. The specific characteristics of the Belt and Road Initiative (a project proposed by one country, which produces effects on a global scale, with a special focus on the infrastructure sector, found in the third chapter) and `The Paris Agreement` (an international non-binding agreement by its formation and structure, but binding by its content, found in the forth chapter) led to the necessity of analyzing them together. The juxtaposition of the two topics is analyzed in the fifth chapter, alongside the leading position of China in both areas of interest and the opportunities that can arise from the linkage of the two topics.
reference(omitted)
