本文是一篇英语论文,本研究旨在调查广西省高中英语新手教师的教学焦虑。根据定量数据和定性数据,本研究得出以下主要结论:首先,广西省65名高中英语新手教师的总体教学焦虑处于中等水平。通过三个维度的比较,教学前阶段的平均值最高,这表明大多数教师在教学前都有中等程度的教学焦虑。
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Background of the Study
An associate professor of psychology at Bond University in Australiaanonymously surveyed 166 Australian teachers (age ranged from 22 to 65 years),recording their information about the workload, work environment, financial situationand sources of stress (Nan Xiaopeng, 2019). The survey found that more than half ofthe teachers had anxiety, and nearly one in five felt depressed. Research conducted byBrog and Riding (1991) also showed that about one-fifth to one-third of surveyedteachers considered their work as being either very stressful or extremely stressful.Thus, it can be seen that teacher anxiety cannot be ignored, especially for noviceteachers. Hu Yanqin (2006) believes that novice teachers, as a special group, will facemuch more difficulties in the new teaching environment compared with other teachers.Novice teachers are at the beginning of their professional development. Comparedwith experienced teachers, novice teachers should not only adapt to the new identity,but also have to adapt to the new environment. In addition, they have to completeheavy teaching tasks. All these conflicts may make them under great physical andpsychological pressure and finally lead to teaching anxiety. Professor Ye Lan(2001:289) once said, “A person’s teaching experience in the first year will have agreat impact on his or her teaching effectiveness and will last for many years; it willalso affect his or her teaching attitude, which will regulate his or her teachingbehavior in the next 40 years; and it will also influence whether he or she will chooseto remain in the teaching profession.” Hence, if novice teachers cannot handle theirteaching anxiety well, it may have a negative impact on their career development.
1.2 Purpose of the Study
Based on the relevant literature at home and abroad, this paper usesquestionnaire and interview as the main instruments to study the overall situation ofnovice English teachers’ teaching anxiety in high school in Guangxi Province. Theresearch aims to find out the following issues: (1) the overall situation of teachinganxiety of novice English teachers in high school; (2) difference in terms of gender; (3)difference in terms of educational background; (4) difference in terms of educationallevel; (5) the causes of teaching anxiety of novice English teachers in high school.These findings are supposed to explore the overall situation and causes of noviceEnglish teachers’ teaching anxiety and then this study puts forward some specificsuggestions for novice English teachers in high school to alleviate their teachinganxiety and improve their teaching quality.
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 Definitions
2.1.1 Novice Teacher
The subject of this research is novice English teachers in high school. In orderto clarify the scope of the research subject, it is necessary to figure out what noviceteachers are. According to the classifications of Berliner (1988), there are five stagesin teacher’s professional development. The first stage is novice level, which refers tostudent teachers in normal colleges or teachers in their first year of teaching. Thesecond stage is advanced beginner, which refers to teachers in their second or thirdyear of teaching. The third stage is competent level. In this stage, teachers are thosewho are engaged in teaching over three or four years. The fourth stage is proficientlevel in which teacher’s teaching experience is over five years. The fifth stage isexpert level. Teachers in this stage have at least accumulated ten years’ teachingexperience. Based on the classifications of Berliner, subjects in this research areteachers engaged in teaching within three years.
2.1.2 Teaching Anxiety
Williams (1991) points out that teaching anxiety is a kind of emotionalconstitution occurring in teaching process and its intensity will change or evendisappear with the accumulation of teachers’ teaching experience. He argues that thiskind of emotional trait has a close relationship with teacher’s classroom teaching andother school activities. Professor Gardner and Leak (1994) from Creighton University in America define teaching anxiety as a kind of anxiety that teachers feel when theyprepare and carry out the classroom activities. However, there is no essentialdifference between this definition and the definition of teacher anxiety. As a result, ithas not been widely accepted. Ameen, Guffey and Jackson (2002) think that teachinganxiety refers to the distress that comes either from the anticipation of teaching or theexperiences that occur in the classroom. Teacher anxiety is an upper concept, whichcontains many specific forms of anxiety, such as pre-service teachers’ mathematicalanxiety, communication anxiety, teaching anxiety, foreign language anxiety and so on.Accordingly, teaching anxiety is not equal to teacher anxiety. Teaching anxiety ismore specific and is related to teaching. In China, there is no clear definition ofteachers’ teaching anxiety. Wang Hang (2017) maintains that teachers’ classroomteaching anxiety is mainly a kind of state anxiety, which is triggered by adverseconsequence or specific teaching situations and teachers cannot deal with iteffectively.
2.2 Theoretical Foundations
2.2.1 State-Trait Anxiety Theory
Cattell (1961) put forward the concepts of state anxiety and trait anxiety, but hedid not make further studies on them. Later, Spielberger made a clear definition onthem and developed a complete State-trait anxiety theory (1966,1972,1985) based on the Cattell’s research. He defined state anxiety as a state of anxiety that happensaccidentally in a specific situation with short duration, variable intensity and obviousbody reaction and it is an individual’s response to changing environmental conditionsor environmental pressure. Trait anxiety is a kind of personality trait, which hasrelative stability and individual difference. In the light of Spielberger’s State-Traitanxiety theory (1972), the arousal of state anxiety needs a process. Firstly, individualshave to evaluate the external stimuli. If they evaluate external stimuli as a threat tothemselves, then the state anxiety will be activated. The degree of threat individualsexperience will have an impact on the magnitude of state anxiety. Meanwhile, theduration of state anxiety depends on the length of time that threat exists and similarexperience. Secondly, anxiety experience will be affected by individual trait anxietybecause different individual trait anxiety will have different anxiety reactions even inthe same situation. Thirdly, when confronting anxiety, individuals will take action toavert or reduce anxiety to the lowest level and what kind of methods they will chooserelies on their own defense mechanism. This process will ultimately result in theexpressions of external act of anxiety. At last, two different feedbacks may affectindividual’s cognitive appraisal. One feedback is that the unpleasant experiencebrought by sensation and cognition will feed back to individuals. As a result,individuals will take a series of actions to lower state anxiety or avoid threats in orderto change their cognitive appraisal. During this process, although cognitive appraisalis at a core position, it is also affected by trait anxiety.
Chapter 3 Research Design.................................. 16
3.1 Research Questions........................................ 16
3.2 Research Subjects........................................16
Chapter 4 Results and Discussion...................................................20
4.1 General Situation of Teaching Anxiety....................................... 20
4.1.1 Data Analysis of Pre-teaching Anxiety..................................... 21
4.1.2 Data Analysis of While-teaching Anxiety.............................................24
Chapter 5 Conclusion.............................................50
5.1 Major Findings of the Study................................................ 50
5.2 Implications of the Study........................................ 51
Chapter 4 Results and Discussion
4.1 General Situation of Teaching Anxiety
According to the results analyzed by SPSS 23, among the 65 valid questionnaires,the mean value is 66.89, its standard deviation is 9.215, the maximum value is 90 andits minimum value is 50. The following Figure 4.1 is the distribution of the scores ofnovice English teachers’ teaching anxiety.
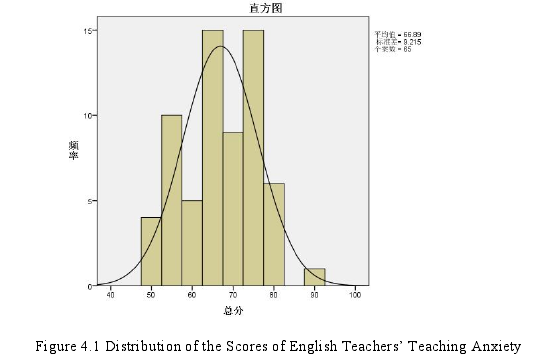
Since the questionnaire is divided into three dimensions, namely pre-teaching,while-teaching and post-teaching, the author calculates the average and standarddeviation of each dimension in order to figure out the level of teaching anxiety in eachdimension. In this research, the level of novice English teachers’ teaching anxiety willbe divided into low level, medium level and high level. As mentioned before, thequestionnaire adopts five Likert-Scale, so the median is 3. Consequently, the lowlevel is less than 3. The medium level is between 3 and 4 while the high level is morethan 4. From Table 4.1, it can be seen that the general picture of the teaching anxietyis 3.041, which is more than 3. Thus, the overall situation of novice English teachers’teaching anxiety is at a medium level. As for the three dimensions, the mean value ofpre-teaching is the highest. It reaches 3.180 which means that it is in the medium level.The mean value of the while-teaching and post-teaching are 2.996 and 2.952respectively which means the stage of while-teaching and post-teaching is at a lowlevel. From the mean values of the three dimensions, it can be found that teachinganxiety of the while-teaching and post-teaching is very close. It reflects that mostsubjects have a medium level of teaching anxiety before teaching, but their teachinganxiety will go down during and after teaching.
Chapter 5 Conclusion
5.1 Major Findings of the Study
This study is to investigate the teaching anxiety of novice English teachers inhigh school in Guangxi Province. In light of the quantitative data and qualitive data,the study concludes some major findings as follows:
First of all, the overall teaching anxiety of the 65 novice English teachers in highschools of Guangxi Province is at a medium level. By comparing the three dimensions,the mean value of the stage of pre-teaching is the highest, which indicates that mostteachers have a medium level of teaching anxiety before teaching. The reason is thatthere might be many uncertainties for teachers to take into consideration beforeteaching. Therefore, most novice English teachers will feel anxious when preparingtheir lessons. As for the while-teaching and post-teaching, both of them are at a lowlevel. In these two stages, novice teachers’ teaching anxiety will be influenced byexternal factors. For example, they will feel anxious when they are observed by otherteachers or when there are unexpected questions raised by students. They might alsobe afraid that students give low marks on their teaching evaluation.
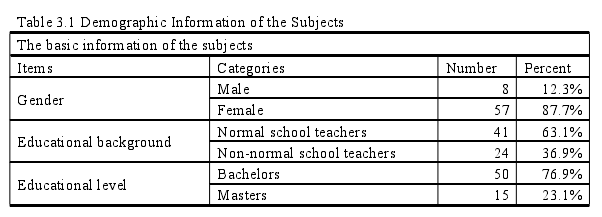
Second, this study aims to find out the difference in terms of gender, educationalbackground and educational level of novice English teachers. According to the dataanalysis, there is no significant difference between male teachers and female teachers.But from the data, it can be seen that the mean score of female teachers is higher thanthat of their counterparts. It can be speculated that male teachers might be good atdealing with stressful teaching situations compared with female teachers. When itcomes to the difference in educational background, there is still no significantdiscrepancy. The mean values of the normal school teachers and non-normal school teachers are 2.998 and 3.111 respectively, which indicates that normal school teachersare at a low level of teaching anxiety while non-normal school teachers are at amedium level. Although these two groups are at a different level of teaching anxiety,their means are very close. And it is noteworthy that the mean scores of non-normalschool teachers are higher than those of normal teachers in all dimensions. As for thedifference in educational level, there is also no distinction between bachelor andmaster but there are some factors that will influence their teaching anxiety, whichleads to a result that the level of teaching anxiety of master is lower than that ofbachelor. From the contrastive analysis, it also can be seen that teaching anxiety ofpre-teaching is always at a medium level no matter in which group.
reference(omitted)
