本文是一篇英语论文,本研究旨在探讨高中生英语学习中的非智力因素。本研究旨在探讨非智力因素对高中生英语学习的影响。本研究通过以下问卷的回答收集数据:高中生英语学习中的非智力因素。共收集310份问卷,其中295份被测为有效问卷,295名高中生参加了本研究。
Chapter1 Introduction
1.1 Research Background
With the advent of industrialization and globalization throughout the world, communication and cooperation, culturally or economically, between nations are becoming closer and deeper. As we can see, the age at which children learn English is getting younger, and English learning has played a more important role in foreign language teaching as an unstoppable expansion trend.
In 2011, the emphasis of the Teaching Requirements for Senior Middle school Students Curriculum is not only put on developing students’ a certain level of comprehensive language competence, but also cultivating their cognitive ability, personality, optimistic attitude and evaluating their development fairly from an all-round perspective. As we can see, the non-intelligence factors (interest, motivation, will, requirements etc) are the focus of new curriculum among the many aspects which might affect language ability of the students in senior middle school. However, the defects that exist in the traditional junior English classroom are obvious.
The main reason is that the examination-oriented education has seen a long history. Thus more attention is placed on the teaching of linguistic knowledge and grammar aspect in English class, the development of learner’s linguistic competence is overlooked. Besides, rarely consider the differences of individual learners, so teachers can’t find the interest of each student and then explore their potential. To change such a situation, teachers should take some effective teaching methods to strengthen students’ interest and cultivate their non-intelligence factors in studying English.
.................................
1.2 The Purposes of Research
On the basis of the prior researches, this study employs the quantitative methods with questionnaire. In order to investigate how non-intelligence factors (motivation, emotion and will, interest, personality) influence the English study of senior middle school students. The collected data are analyzed by the Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS, version 20) in a hope to find out the main causes influencing the students’ nonintelligence factors in the process of their English learning and to offer some useful advice to senior middle school teachers and students who may get a better improvement on English teaching and learning. The study aims to find out the overall situation of senior middle school students’ non-intelligence factors in English study, and to find out if there is any gender and grade difference in senior middle school students’ non-intelligence factors by using independent t-test.
....................................
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 Description of Non-intelligence Factors
There are two parts in this section, which are definitions and functions of non-intelligence factors that effect on English learning. They will be presented in detail respectively as follows.
2.1.1 Definitions of Non-intelligence Factors
With the continuous development of domestic research on non-intelligence factors and abundance of related theories, the debate on the concept of non-intelligence factors has not stopped. Non-intelligence factors are firstly proposed by an American psychologist W.P. Alexander. He generalized non-intelligence factors from the psychological structure of intellect and intelligence behaviors as follows: (1) All kinds of intelligence level from simple to complex reflect the function of non-intelligence factors. (2) Non-intelligence factors are a necessary part of intelligence behaviors. (3) Non-intelligence factors could not take place of the basic ability of intelligence factors, but could restrict the intelligence. (Alexander, 1935)
In the early 1980s, the concept of non-intelligence factors was introduced into China. Professor Yan Guocai divides non-intelligence factors into three gradations. The first one is general sense that all psychological factors can be called non-intelligence factors that effect on learning besides intelligence factors. The second one is non-intelligence factors in narrow sense which are made up of 5 psychological elements, such as motivation, interest, affect, will, and personality. The last one is detailed intellectual factors which have 12 factors, namely, achievement motivation, learning desire, learning enthusiasm; self-confidence, self-esteem, enterprising spirit; sense of responsibility, sense of obligation, sense of honor; self-control, self-independence and perseverance. (Yan Guocai, 1987)
....................................
2.2 Theoretical Foundation of the Present Study
2.2.1 The Input Hypothesis
Second language acquisition relates to the process of acquiring proficiency after the native tongue. In linguistic learning, people usually investigate its procedure and expect that relevant information about it can be used. And the main purpose of SLA is to explain and describe how the learner can obtain the language ability and skills. People research it mainly from two areas, learner-external factors and learner language. The study of SLA may form in the late 1960s and early 1970s. A variety of SLA researchers debate the relationship between acquisition and studying and how they work in language courses. In 1982, American linguist S.D. Krashen put forward that there are two related systems in terms of language function. He argued that one is the acquired system that is subconscious. The other is the learned system which refers to conscious language knowledge. (Krashen, 1982)
At the beginning of 1980s, Krashen put forward famous “The Monitor Theory”, it includes the Natural Order hypothesis, the Acquisition-learning hypothesis, the Monitor hypothesis, the Affective Filter and Input hypothesis. Krashen explained these five hypotheses in detail and affirmed the critical role of the input hypothesis (Krashen, 1982: 9).
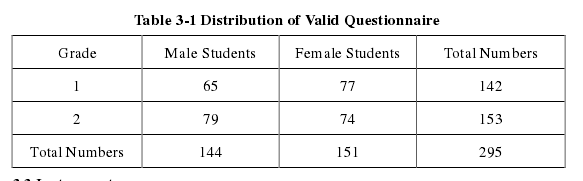
Table 3-1 Distribution of Valid Questionnaire
.....................................
Chapter3 Research Design .............................................. 17
3.1 Research Questions ..................................................... 17
3.2 Subjects ................................................ 17
Chapter 4 Research Results Analysis and Discussion................................. 23
4.1 Overall Description of Senior Middle School Students’ Non-intelligence Factors in English Learning ................................. 23
4.1.1 Achievement Motivation in English Learning .................................... 24
4.1.2 Cognitive Interest in English Learning ................................. 26
Chapter 5 Implications ...................................... 46
5.1 The basic knowledge of linguistics ......................................... 46
5.2 The roles of the teacher and students ............................ 46
Chapter 5 Implications
5.1 The basic knowledge of linguistics
The two most important questions in language teaching are: what to teach and how to teach. Knowledge of linguistics can give a language teacher a better understanding of what to teach because linguistics is about the internal structure of a language. Grammar, the social and psychological aspects of language use, and the relationship among languages, both in history and in the present day, are all included in linguistics.
“The ‘theory’ of language with which the teacher operates may not be consciously formulated; it may simply be implicit in the teaching traditions, in the concepts employed to talk about languages, in the way textbooks are arranged, or in the content and formation of dictionaries and grammars; but it is hardly imaginable that a language could be taught without some underlying conception of the general nature of language” (Stern 1983: 119). “The value of linguistics is that by increasing his awareness of language. It makes him more competent and therefore become a better language teacher” (Wilkins 1972:229). Obviously, all these are necessary for a good teacher of foreign languages.
Table 3-2 Internal Reliability and Validity of the Questionnaire for Senior Middle School Students
............................
Chapter 6 Conclusion
6.1 Summary of Major Findings
This investigation is conducted to look into senior middle school students’ non-intelligence factors in English learning. It aims at exploring the effect of non-intelligence factors on senior middle school students’ English learning. In this study, the data is collected through the responses of the following questionnaire: Non-intelligence Factors for Students of the Senior Middle School in English Learning. After 310 questionnaires were collected, 295 of them were measured as valid, so 295 senior middle school students participate in the study. Through the investigation, the three research questions proposed at the beginning of this thesis can be answered and the major findings are summarized as follows.
The first research question examines the overall situation of senior middle school students’ non-intelligence factors in English learning. The results of the present study show that among the five dimensions of non-intelligence factors in English learning, students have a relatively high level in cognitive interest and achievement motivation then followed by learning anxiety, will to execl others and learning stamina. The mean score of the whole questionnaire is 3.1798, indicating that senior middle school students’ non-intelligence factors are at a relatively medium level in English learning.
The second research question examines the gender and grade difference of senior middle school students’ non-intelligence factors in English learning. The results of the present study show that the overall situation of senior middle school female students’ non-intelligence factors is slightly higher than male students. Taking the frequencies of the specific items into consideration, the female students’ non-intelligence factors are higher than male students in achievement motivation, learning anxiety and will to execl others. In terms of grade difference, the overall situation of senior Grade one students’ non-intelligence factors is higher than Grade two and the difference is not significant in English learning. But the grade difference of learning anxiety is extremely significant and the Grade one students are relatively anxious in English learning. For Grade one students, it is not easy to adapt themselves to their new classmates and teachers. Therefore, fear of teacher’s and their classmates’ laugh or defiance, lack of confidence and high expectation of teacher and parents are the main causes of their higher learning anxiety.
reference(omitted)
