本文是一篇英语论文,本研究的结果可以总结如下:首先,根据问卷调查和访谈的结果,可以得出英语学习动机处于中等水平的结论。T市高中确实存在着学生的消极情绪,并且在学生中有一定的发展趋势。T市高中生的学习积极性或多或少都有所下降。尽管学生的积极性没有严重下降,但在英语学习中,积极性下降是不可忽视的。教师和学生都应该意识到英语学习中去积极性的负面影响,努力减少英语学习中的去积极性。
Chapter One Introduction
1.1 Background of the Study
There is no doubt that English, as an international language tool in the world, plays an important role in communication and cooperation between countries. And that’s why all the students in China learn English as a foreign language. In most districts of China, English is a basic and necessary subject from primary schools to universities. In other words, students are always keeping in touch with English learning. Senior middle school English education really plays an important part in the whole English education, but English learning demotivation is found among students in senior middle schools.
At present, a series of English teaching and learning reforms are being explored in our countries to improve students learning motivation, to better meet the needs of social communication and cooperation. For example, Chinese educational scholars focus on the reform of teaching methods, English curriculum standards, English textbooks, English for the Entrance Examination of College and so on. The new Middle School English Curriculum Standard from Ministry of Education put forward to “core literacy” for the first time. The connotation of English subject core literacy are made of three main aspects (language ability, thinking quality, and cultural awareness) and two key points (learning ability and emotional attitude). The new curriculum standard emphasizes that emotional attitude is the key to cultivate core literacy and the lubricant for other literacy. In language learning, the growth and development of students rely on motivations that are closely linked to their emotional attitudes. Only when students’ emotional attitudes are mobilized can students have the internal driving force for development. From this point of view, learning motivation plays an important role in the learning process, and the strength of learning motivation directly affects the learning effect.
............................
1.2 Purpose of the Study
Motivation is one of the most significant parts of emotional attitude in foreign language learning. Dornyei (1994) referred that learning motivation, which was considered to be a key factor of success in foreign language learning, usually has a great effect on the learners’ performance. Anyone who has stronger learning motivation will work harder and get greater achievement. In reverse, the learners will have negative performance if they are demotivated. Most of the front-line English teachers find that their students seem to be less interested in learning English. Their students often suffer distractions in class and low scores in examinations. The thesis is to investigate the senior middle school students in T City, Guangdong Province that whether they get demotivation in English learning by the means of questionnaire and interview. According to the results of the investigation, the thesis explores the current situation of English learning demotivation, analyzes the differences of English learning demotivation between senior one and two students, between male and female students, seeks for the main demotivating factors in English learning, and proposes some suggestions and strategies of improving students’ motivation at last.
There are two main purposes of the study. The first aim is to help students raise their interest in learning English, regain confidence in learning English, experience the pleasure in learning English, and enhance academic performance in learning English. The second one is to help teachers know more about their students’ needs and difficulties, analyze the main reasons for students’ learning demotivation, search for efficient methods in teaching and learning, and solve the problems of teaching and learning. In a word, the thesis aims to offer some help of improving students’ learning state and academic quality level in English.
...........................
Chapter Two Literature Review
2.1 Description of Demotivation
The definition of demotivation and the demotivating factors are presented in this section.
2.1.1 Definition of Demotivation
Motivation is thought to be a crucial factor in foreign language acquisition. When the literature is reviewed, it is seen that there are quite a large number of motivation-related studies in the field of learning foreign language. In the past, the researchers concentrated their views on the positive motivation instead of negative aspect. However, more and more researches focus on demotivation in the field of second language learning and teaching recently. Demotivation is the branch aspect of motivation that has been introduced as a new area of research in second language learning since the 1990s but it has received inadequate attention. Many scholars raised the definition of demotivation and expanded the deep meaning of demotivation.
Different researchers emphasize on the definition of demotivation differently. On one hand, the definition of demotivation was referred to the force from external and internal aspects to decrease motivation in learning. Dornyei (2001) identified demotivation as “the specific external forces” that decease or diminish the motivation in learning. In Dornyei’s theory, it can be seen that the external forces, such as the learning environment, the learning equipment etc. may cause the decreasing or decreasing the learners’ intention or behaviors in their second language acquisition. Another definition was given in the area of instructional communication by Zhang (2007) to demotivation as “the force that decreases students’ energy to learn and/or the absence of the force that stimulates students to learn”. Furthermore, some researchers found that demotivation may also be introduced by the internal forces which are confidence, anxiety, self-determination and so on. For example, Sakai and Kikuchi (2009) viewed that the internal forces were the important factors that cause the learners’ attitude or behavior to give up their learning in the second language acquisition. Kikuchi (2011) expanded Dornyei’s definition of demotivation as “specific external forces” and redefined it by adding the internal factors “the specific internal and external forces that reduce or diminish the motivational basis of a behavioral intention or ongoing action”. Ghadirzadeh (2012) stated that demotivation is a decrease or drop in level of motivation starting from an eternal force before being an internalized process.
...............................
2.2 Theoretical Basis of Research
Demotivation is the branch of motivation which belongs to the area of psychological research. It has decades of years since demotivation was introduced into the area of foreign language learning. There is no specific theory about demotivation but some theoretical basis of motivation and demotivation can be sorted.
From the literature published online, the research on foreign language learning motivation was first introduced by Gardner and Lambert (1960). Then they put forward the theory of second language learning motivation which contained motivation of integration and motivation of tools. Deci and Ryan (1985b) proposed a theory of internal and external motivation and a theory of self-determination motivation, which were considered to be significant in the study of foreign language learning. Based on the previous researches, Dornyei also proposed three-level model of foreign language learning motivation, evaluating motivation from three levels which are from learners, language, and learning situation. In addition, a theory of goal setting and task performance raised by Edwin Locke and Gary Latham was put into the motivation theory.
Some related theories such as Dornyei’s motivation and demotivation theory, Self-Determination Theory, and Goal Theory can be regarded as the theoretical basis of motivation and demotivation.
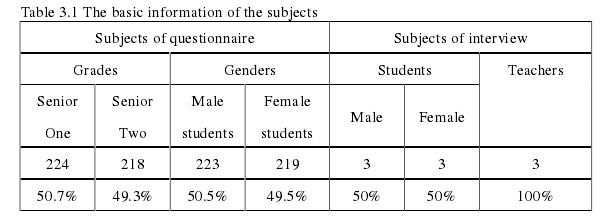
Table 3.1 The basic information of the subjects
...............................
Chapter Three Research Methodology .................................. 24
3.1 Research Questions .............................................. 24
3.2 Research Subjects .............................................. 24
3.3 Research Instruments ............................................. 25
Chapter Four Results and Discussion .............................. 30
4.1 Results of Questionnaire ...................................... 30
4.1.1 Current Situation of English Learning Demotivation of Senior Middle School Students in T City .......................... 30
4.1.2 Differences of English Learning Demotivation ........................ 34
Chapter Five Conclusion and Implications ......................... 60
5.1 Major Findings ....................................... 60
5.2 Pedagogical Implications ........................................ 61
Chapter Four Results and Discussion
4.1 Results of Questionnaire
A questionnaire is designed to investigate the current situation of English learning demotivation, tell differences of English learning demotivation in grades and genders, and explore the domain demotivating factors. With SPSS 21.0, the results of questionnaire are collected and analyzed in this section.
4.1.1 Current Situation of English Learning Demotivation of Senior Middle School Students in T City
The first question of the research is to investigate the current situation of English learning demotivation of senior middle school students in T City. In the second part of the questionnaire, ten items are designed to investigate students’ current situation of English learning demotivation. Table 4.1 shows the descriptive statistics of the current situation of students’ demotivation in T City.
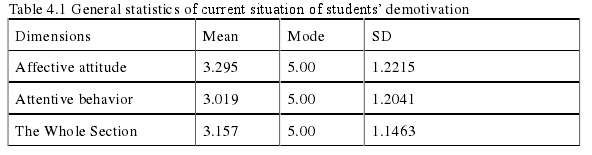
Table 4.1 General statistics of current situation of students’ demotivation
...................................
Chapter Five Conclusion and Implications
5.1 Major Findings
This study aims to investigate the current situation of senior middle school students’ English learning demotivation in T City. Through the questionnaire with good reliability and validity and interviews, all the research questions have been answered fully. The findings of the study can be summarized as follows:
First of all, according to the results of the questionnaire and interview, it can be concluded that the English learning demotivation is at a medium level. Demotivation really exists in senior middle schools of T City and it has a developing tendency among students. The senior middle school students in T City have been demotivated more or less. Though the students are not seriously demotivated, demotivation cannot be neglected in English learning. Both teachers and students should be aware of the negative effect of demotivation and try to decline the demotivation in English learning.
Secondly, this research also tries to investigate the differences of English learning demotivation between senior one and two students, between male and female students. Through the analysis with Independent Sample T-test, it is found that there is no significant difference between senior one and two students. Both of the two grade students are demotivated to a certain degree. However, there is significant difference between male and female students. Male students are more demotivated than the females.
Thirdly, the research aims to explore some main factors that cause English learning demotivation of senior middle school students in T City. In this study, the demotivation factors can be categorized into four dimensions: learners-related factors, teachers-related factors, society-related factors and environment-related factors, trying to find out the main factors that cause the students’ demotivation in T City. After investigation and analysis, learners-related factors take a relatively large proportion in students’ English learning demotivation attribution. Most of the students attribute the demotivation to the internal factors of their learning difficulties and lack of learning strategies. Few students attribute their demotivation to their teachers in this research. Although the students consider teacher-related factors as the least influential causes, it does not mean that teachers take no responsibility on students’ English learning demotivation.
reference(omitted)
