Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Formulation of the Research Problem
Recently, as a main component part of teaching reform in High Education, collegeEnglish teaching reform has attracted widely public attention for two reasons,importance and inelasticity. Importance refers to the large quantity of college Englishstudents and the quality of higher education while inelasticity indicates it can‘t satisfyexpectation from students and society.The Outline of China‘s National Plan for Medium and Long-term EducationReform and Development (2010-2020), announced by Ministry of Education of thePeoples‘ Republic of China, has presented a blueprint for China‘s education reformand development for the next 10 years. According to the Plan, Educationaldevelopment should be future-oriented. It is not only necessary to solve pressingproblems and meet practical needs, but also necessary to look into the future andclearly understand our long-term objectives and tasks; it is not only necessary to trainhuman resources to meet our present development needs, but also necessary to trainmore talents for our economic and social development in the future Furthermore, the Plan points out that education reform and developmentshould always be student-oriented and focused on quality education. So, teachersshould adopt a learner-centered approach, promote overall development of thestudents and help them develop a sense of social responsibility, innovative spirit andgood problem-solving skills.In addition, College English Curriculum Requirement (2007) points out thatcollege English Education need develop students‘ English proficiency of comprehensive language application, including listening, speaking, reading andwriting ability (Shu, 2012). In addition, to enhance the capacity of independentlearning is also addressed. However, the traditional teaching model can‘t satisfy therequirements.
…………
1.2 Purpose and Significance
The Writing Workshop at Hunan University indicates the possible change thatemphasizes hand-on experience rather than indirect experience in higher education.Language teaching has developed from the previous Grammar- Translation Approach tothe Communicative Approach and now to the latest popular Task-Based LanguageTeaching. Unlike the traditional method whose focuses are the language forms,task-based language teaching stresses the active, individualized learning process andsolving problems, Task-Based Language Teaching Approach is always organizedaround a variety of tasks which are related to the real life and composed of chains ofactivities psychologically selected, graded and sequenced. Writing Workshop attaches importance to the improvement of all language skillsthrough task experience; additionally, all tasks are selected based on the needs ofstudents‘future careerdevelopment. Asonekindofreform, the WritingWorkshop maybecome a good example in the national implementation. As the core of task-basedteaching, task complexity influences students‘ performance and behavior. So, it isnecessary to explore the factors contributing to task complexity in writing workshop.
………..
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 Task and Task Complexity
Task, as the core of task-based approach, has been defined by many researchers(Long, 1985; Wood, 1986; Campbell, 1988; Nunan, 1989, 2005, 2006; Skehan, 1996,2003; Robinson, 1995, 2001; Willis, 1996; Braarud, 2001; Ellis, 2000, 2005, 2006,2009; Nunan, 2004) from different perspectives. Nunan (2006) draws a basicdistinction between real-world or target tasks, and pedagogical tasks. Target task, asthe name implying, refers to the use of language outside the classroom. Pedagogicaltasks are those that occur in the classroom situation.Long (1985) frames his approach to task-based language teaching in terms oftarget tasks while other researchers may regard tasks as the performed and usefulaction for the classroom setting.Task-related research has appeared extensively in the social and behavioralscience literature. However, there is limited consensus on the understanding of a taskand its characteristics in the literature (Hackman, 1969; Wood, 1986). Eightrepresentative definitions drawing from the comprehensive literature review ontask-based instruction are given below.
………….
2.2 Pervious Research on Task Complexity
In the literature, task complexity is always viewed from both objective andsubjective perspectives.The objective perspective considers task complexity is related directly to taskcharacteristics and independent of task performers, which has been supported by anumber of researchers (e.g. Rouse and Rouse, 1979; Wood, 1986; Campbell, 1988;Bonner, 1994; Harvey, 1998; Braarud, 2001; Greizer, 2005; Braarud, 2001). Objectivetask complexity is based on the assumption of the existence of an objective taskexternal to and independent on task performers and the existence of a ―detached,omniscient observer ‖ (Wood, 1986). In a word, task complexity is often used todistinguishobjective task complexity from task solver‘s experience oftask complexity,that is, subjective task complexity (Braarud, 2001).From the perspective of subjective, task complexity is regarded as a conjunctproperty of task and task performer characteristics, which has been widely supported byresearchers from the information seeking domain (e.g. Braaud, 2002; Braarud &Kirwan, 2011). Braarud & Kirwan(2011) stress that subjective task complexity is thelevel of task solver‘s perception about the complexity of the task, which is a outcomeof the operator‘s training, experience, and procedural support, but mainly his trainingand experience.
………..
CHAPTER 3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY.....41
3.1 RESEARCH QUESTIONS....41
3.2 RESEARCH FRAMEWORK........41
3.3 POPULATIONAND SAMPLING.........43
3.4 Instrument design ....43
3.5 Data Collection........44
3.6 Data Analysis....45
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION ........47
4.1 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS OF THE SAMPLES AND ITEMS ....47
4.1.1 Descriptive Statistics of the Samples .........47
4.1.2 Descriptive Statistics of items......47
4.2 VALIDITYANALYSIS OF THE ORIGINALQUESTIONNAIRE ......48
4.2.1 Items Screening.......48
4.2.2 Validity analysis ......51
4.3 FACTOR EXTRACTION......52
4.4 NOMENCLATURE OF FACTORS .......56
4.5 THE WEIGHT OF EACH FACTOR.....57
4.6 QUALITATIVE DATAANALYSIS.......58
4.7 RELIABILITYAND VALIDITYOF THE NEW SCALE.......62
4.8 DISCUSSION.......64
Chapter 4 Results and Discussion
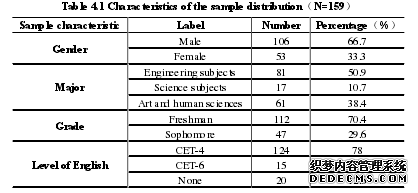
It is the aim of this paper to identify and evaluate latent factors that are notdirectly observed but contributes to creative task complexity in writing workshop. So,in this chapter, a series of statistic analyses will be conducted on the data collectedfrom writing workshop by research questionnaires survey. Efforts will be concentratedon revealing factors contributing to task complexity. Table 4.1 illustrates the characteristics of the sample distribution. As displayed inthe table 4.1, 66.7% of the sample is male and 50.9%of them majors in engineeringsubjects. A total of 124 out of 159 samples have passed CET-4, representing a rate of78 %.
…………
Conclusion
In this chapter, it primarily summarizes factors contributing to creative taskcomplexity in writing workshop. Then, limitations of the present study are admittedand suggestions are put forward for further research at the end. This study employs factor analysis to explore and identify the grouping ofvariables revealing associations between them, which in context provides importantdirections on the predominant perception among students. The result obtained by thestudy is allowed to define an explanatory and ordinal construct of factors, which canbe divided into seven groups.The first group refers to clarity and mismatch of input, including course centerwebsite, teaching assistant and presentation. The second group refers to the conflict ofgoals, such as written communication skills, teamwork cooperation capacity andcommercial English writing ability. The third factor is clarity of process. The forthfactor concerns the quantity of product (minute, E- mail and report). Mismatch ofteachers‘ illustration belongs to the fifth factor while coordination of team work isclassified into the sixth factor. Familiarity with topic is arranged to seventh factor.
..........
Reference (omitted)
