Chapter One Introduction
1.1 Background of the Study
The core idea of the new course reform is student-centered, which aims at makingefforts to change the learning style of students and to cultivate the students’ innovation spiritand practice ability. Classroom teaching is an important link in the teaching process and it isalso the main channel to culture students’ capacity. Teaching design is a kind ofpre-arrangement or planning for classroom teaching and an essential step to optimize the idealteaching. No teaching design, there can be no teaching optimization.The traditional instructional design is teacher-centered and knowledge-centered.Teachers are dominant, while students are passive recipients of knowledge. Its main form isteaching case. The teaching case emphasizes on teachers’ teaching plan which is madeaccording to the curriculum standards and requirements of textbooks, combined with theactual situation of students, taking a class or a topic as a unit, which is the basis of classteaching.Generally, the plan is closed, which is only known by the teacher, not by students,usually making study a passive acceptance under a circumstance of being not clear of thelearning tasks. Although the plan includes clear teaching objectives, teaching difficulties,main points and teaching methods, it is generally designed from the teachers’ point of view todecide what to teach and how. In practice, it often can not meet the actual needs of classroomteaching, and will easily ignore the cultivation of inquiry process and inquiry ability, ignorestudents’ practice competence, neglect the training of cooperation ability, thus it can not fullylet students play the main role, and finally lead to low learning efficiency and poor teaching quality.
………..
1.2 Research Questions
Traditional studies have paid their attention to teachers’ teaching method or textbooks,while seldom concentrate on the main role of learning –students. This paper aims to find amore effective teaching model, thus to better connect teachers and students together, whichplans to apply the constructivism to English teaching in a public county junior middle schooland tries to investigate the following questions:
1. What are the differences between the traditional teaching model and the new modelthis paper tries to study?
2. Can constructivism-based English teaching model more effectively improve students’English proficiency and teaching efficiency as compared with traditional teaching model?
3. As for the second question, if no, why? If yes, how does it play the role and what arethe effects of the new teaching model under the application of constructivism?
4. What are the principles of designing the new teaching model to help students study?
………
Chapter Two Literature Review
2.1 Researches on Teaching and Learning Case Integration
Teaching case is a common integration text which integrates the traditional teacher’slesson plans with the actual situation of students’ learning and the problem of practice forboth teachers and students in class. It is also one of the common carrier of inquiry activitybetween teachers and students that integrates teachers’ lesson plans, students learning,hierarchical teaching and extends. First, teachers have to prepare a lot of data, then accordingto the students’ prior knowledge level and learning ability, offer guidance on students’autonomous learning, showing the new knowledge to students in the form of questions, and atthe same time, manifest the philosophy of first learning after teaching and the unity ofteaching and learning, which is the core of the teaching case. Teaching case teaching is a mode that makes the teaching case as a carrier, a teachingactivity that students under the guidance of teachers in a planned and targeted way toindependently explore knowledge. “Teaching” of the teaching case reflects the teacher’sleading role in the teaching process, while “Learning” the main body role of students inlearning. Teacher’s teaching in the process will be targeted, in order to successfully achievethe teaching goal. So in teaching case teaching, teacher’s main task is to guide students tolearn, to evaluate and offer guidance on the learning time, the content and methods, inspirestudents’ thinking, etc.
………..
2.2 Researches Relevant to Teaching Model
In the course of English Language Teaching, Wang Qiang has opened up a chaptertalking about the relevant knowledge about the research on English teaching in the first andthe second edition. She thinks, as for a teacher lack of experience or experienced, writing alesson plan is an important link in the process of preparation before class. At the same time, she also thinks writing lesson plans should be of diversity, flexibility, learnability andconsistency. She points out that parts of the English lesson plan includes: the student’sbackground, teaching goals, language contents and skills, phases and steps, teaching methods,curriculum summary, selection of reflection, after-school activities and assignments. Amongthem, Wang Qiang especially emphasizes on the difference between phases and steps. Shethinks, phase refers to the main content of the language discipline teachers implement in theteaching process. Steps refer to the specific contents. At the same time, she also pays attentionto the reflection after class. She thinks writing reflection is the only part to finish after class inthe process of teachers’ teaching, in this part, teachers can write down profit and loss in theclassroom after the class, including the whole process of teaching, students’ performance inclass, the tiny link to ignore when preparing, satisfying points in the process of teaching, aswell as the need to continue to improve and the places to pay special attention to, and so on.In the section about lesson plans in the book English Teaching Method (1999), Gu Yueguofirst investigates the role of the lesson plan.
……….
Chapter Three Theoretical Framework.... 23
3.1 Definition of Constructivism ......... 23
3.2 Constructivism Learning Theory......... 24
3.3 Constructivist Learning Environment ....... 25
3.4 Constructivism-based Teaching .... 26
Chapter Four Methodology...... 27
4.1 Research Subjects ........ 27
4.2 Research Instruments......... 27
4.2.1 Test......... 28
4.2.2 Questionnaire ..... 28
4.3 Research Procedure ..... 29
4.4 Teaching-case-based Teaching...... 29
4.4.1 Teaching Plan..... 30
4.4.2 Teaching Material .... 32
4.4.3 A Sample Teaching........ 32
4.5 Data Collection and Processing..... 37
Chapter Five Data Analysis and Discussion ......... 39
5.1 Analysis of the Results of Pretest and Posttest...... 39
5.2 Analysis of the Result of Questionnaires ........ 40
Chapter Five Data Analysis and Discussion
5.1 Analysis of the Results of Pretest and Posttest
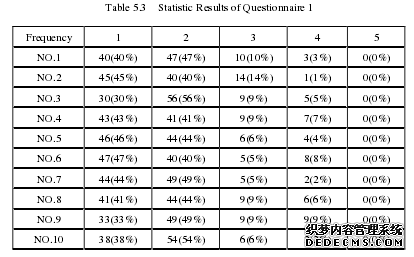
Group A and B is divided into the same level of two control groups based on students’English grade. In the first two weeks of the experiment, the teacher only offers group A theteaching case, auxiliary self-study, while students of group B study by themselves accordingto the textbook and teaching material only. Two weeks later, the teacher selects a topic, andthen gives them the pretest on the basis of students’ self-study before the experiment. As can be seen from the above images and data (Table 5.1 and Table 5.2), in the earlyexperiments, although the group A only follow the teacher using two weeks of teaching case,with the help of the teaching case, on the average it has had a significant difference from thesame level group B, and students’ self-study discrete case in group B is bigger. Thus, theteaching case plays a certain role in guiding students how to grasp the emphases anddifficulties of learning content, how to better understand the new knowledge, and apply to theconcrete problem solving.
………..
Conclusion
It has been proved that in the English teaching of junior middle school, the teachingcase in teaching model, is in line with the new curriculum standard and it advocates theindependence, cooperation and inquires learning style, and realizes the basic goal of languagelearning, namely learning a language is for communication.The content of the teaching case design fully embodies the principle of “teachingdefines learning”, highlights the subjectivity of the students. Through a series of the design ofthe student activities, it well promotes the student to integrate the old and new knowledge,and improves the existing English knowledge structure. At the same time, the teachers’teaching serves the students learning, and guidance of teachers’ wisdom prompts students tobe good at discovering problems, boldly to resolve the problem, and students’ autonomouslearning ability has improved significantly. The design intent column in the teaching case andthe teachers’ auxiliary process in class when students come to the important and difficultpoints, have well strengthened the guidance of students’ learning methods.
…………
Reference (omitted)
