Chapter One Introduction
1.1 English Immersion Education in China
In tiie process of finding an adequate English teaching method to improvelearners' communication skills,immersion education w沾 first brought into tiiemainland of China in 1997 in a workshop conducted in XT an. The CanadianImmersion Program was introduced to Chinese professionals back then. Thetheoretical principles as adopted in the French Immersion were very attractive toChinese scholars. The success of the French immersion stimulated the Chinesescholars to pursue the possibilities of fransplanting this model to China (Qiang &Kang,2007). If successftil, the IE programs would enable learners to learn Englishin a manner similar to their mother tongue acquisition. They could also acquire the second language easily and naturally in a meaningful context through integrationof language learning with subject knowledge (Qiang & Zhao, 2001).After the workshop,English educators in China started to experiment withthis North American immersion model. In 1998,early English ImmersionPrograms were implemented in elementary schools in several major Chinese citiesas an attempt to expose learners to authentic English input at an earlier age thanhad been in the usual practice. These programs were carried out in elementaryschools in which learners had courses instructed by only the English language forat least half of the school day. These programs aimed at enabling learners todevelop confidence and fluency when speaking English. They provoked task-basedlanguage teaching instead of rote memorization and grammar drills. Researchrevealed tiiat Chinese language learners enrolled in an early immersion programperfotmed significantly better on English oral proficiency, vocabulary,and wordidentification than their non-immersion peers (Zhao, 2007),
………..
1.2 The Structure of the Paper
The paper consists of five chapters.Chapter one is the introductory chapter to describe the background of thestudy. This chapter also introduces the situation of English learning in China andthe context of immersion programs,and describes the events which provide in thisresearch in this chapter.Chapter two is the literature review on studies of language immersioneducation and related theories. It presents the research questions,and explains thedefinitions and conceptual issues of IE as well as &e related findings fromprevious research.Chapter three deals wititi the methodology of the study. The qualitative casestudy approach adopted, the three sample learners selected,and the field workconducted are all described in great detail. Data collection and data analysisprocedures are also explained in this chapter‘In chapter four, the results of the data analysis are presented with the aid oftables and graphs.The research findings are presented in Chapter five. It also presents otherdiscussions together with the suggestions for English education and furtherresearch. It also describes the limitations of this study.
………..
Chapter Two Literature Review
2.1 The Categorization of Immersion Education
In the 1950s,tiie immersion system was developed as a new approach oflanguage education. According to Baker (2006), language immersion is defined asa method of teaching language,usually a second language (L2),in which the targetlanguage is used as both the curriculum content and the meditmi of instruction. InImmersion programs, L2 is the instructional language. Language learners use L2 toexpress new concepts and facts of the subjects taught. Immersion education aimsat achieving learning outcomes in two areas; one is in L2 acquisition, the other isin the learning of subject contentBased on the different degrees of immersion,immersion education iscategorized into three types: Total Immersion, Partial Immersion and Two-wayImmersion. As the name suggests, in Total Immersion almost 100% of the schoolday is spent on learning the L2,meaning tiiat almost all subjects are taught in tiheL2. Partial Immersion means in the program the curriculum is partially taught inthe L2,while Two-way Immersion programs integrate native speakers of twolanguages, providing instruction in both languages for all learners (Baker, 2006).
………..
2.2 The Implementation of Immersion Programs
The first immersion programs were developed in Canada in the 1970s toprovide English-Speaking learners with the opportunity to leam French. In theseprograms, the French language was widely used in history, geography, psychology,physics and physical education class. The learners can master the basic knowledgeof a subject and at the same time acquire the French expressions of the knowledge.This is 'teaching French through the subject and teaching the subject throughFrench' (Snow & Brinton,1998).Since that time, immersion programs have been adopted in many parts ofNorth America, and alternative forms of immersion have been devised. In theUnited States,Immersion programs were mainly carried out in the form ofsubmission which was created for the immigrants from other countries.Submission is a teaching metitiod in which the minority language learners receiveeducation through the majority languages rather than their native tongues. The learners are required not only to learn the majority language but to get accustomedto the culture.However, in such context-reduced classroom,not all the learners can masterthe target language in submission education. Besides the language difficulty,submission also brings problems to the communication and emotion aspects thatlearners encounter. If we compare submission to learning swimming,tiie learnersare tiirown into whole second language environment is what the green hands ofswimming are thrown into the deep water without any swimming skills. They justexperience xips and downs (sometimes use L2 correctly, sometimes incorrectly)and mi^t even get drowned (totally lost in L2) without any lifesaving equipmentand necessary guidance.
………..
Chapter Three Research Methodology......... 14
3.1 Research Aims and Research Questions......... 14
3.2 The Research Design......... 15
3.3 The Research Setting and the Sample......... 16
3.3.1 The Choice of Research Site......... 16
3.3.2 The Selection of Participants......... 17
3.4 The Data Collection Process......... 22
3.5 The Data Analysis Process......... 27
Chapter Four Research Findings and Discussions......... 30
4.1 The Changes in Ellen's Academic Performance in English Learning .........30
4.2 The Changes in Michel's Academic Performance in English Learning......... 39
4.3 The Changes in Tomas,Academic Performance in English Learning ......... 47
4.4 Participants' of Their Improvement in English Competence......... 56
Chapter Five Research Findings and suggestions......... 61
5.1 Research Findings......... 61
5.2 Other Discussions......... 62
5.3 Limitations of the Study......... 64
5.4 Suggestions......... 64
Chapter Four Research Findings and Discussions
4.1 The Changes in Ellen's Academic Performance in English Learning
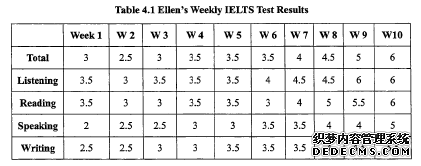
After ten weeks' studying in VCE,Ellen has made some progress in Englishlearning. Specifically,her reading speed has increased, her writing is much clearer,more coherent and logical; and she can also express herself more clearly in class.At the same time,her vocabulary has been enlarged significantly. However,she Still has some difficulties in handling grammar rules, especially when she speaksand writes English. Because of her introvert characteristics, her practice of spokeEnglish is limited. As graph 4.1 shows, Ellen's lELTS weekly test scores are on a rise in the 10weeks in general. Her total score rose from 2 in the first weekly test to 6 in thetenth weekly test, which was a huge improvement in such a short period. I am going to display the changes in Ellen's English listening, reading, speaking andwriting in the following sections.
………….
Conclusions
This study endeavors to address the effect of an Immersion EducationProgram on participants as practiced in an International Department of a highschool in Chengdu, The research questions included:
1. Have the sample students improved their English comprehension skills(listening comprehension and reading comprehension) after theirlearning of English in IE program for a certain amount of time?
2. Have the sample students improved their literacy-based language skills(speaking,writing) after their learning of English in IE program for acertain amount of time?
The current study was carried out as a case study; it was aimed to get anin-depth understanding of the effect of immersion programs on Chinese highschool students. Specifically, I selected three sample students,Ellen,Michel andTomas,who studied in a high school immersion program in Chengdu, as myresearch subjects. During the 10-week field work, I collected data by interviews, observations and examinations of the educational documents. Generally, all threesample students demonstrated improvemeats in their English competence after 10weeks,studying in the IE program.Specifically, in the modified immersion program, the sample students madesubstantial improvement in their English comprehension skills (listening andreading). Their constant exposure to English materials enlarged their vocabularyconsiderably, which in turn led to their further improvement in Englishcomprehension skills.
…………
Reference (omitted)
