Chapter One Introduction
1.1 Background of the study
Through the ages, effective vocabulary learning has long been a main task of collegeEnglish teaching and a big challenge for College students. In the 2007 non-English majors’College English Curriculum Requirements, students at different levels are requireddifferently. At the high level, students need to acquire at least 7,675 words and 1,870phrases, including 2360 active words. At the mid-level, students must acquire a total of6,325 words and 1,270 phrases, including 2200 active words. At the basic level, studentsneed to acquire 4,795 words and 700 phrases, including 2000 active words, which theymust completely comprehend and use fluently in speaking and writing. This provisionillustrates that teachers need to enlarge the number of students’ vocabulary as well asconstruct all kinds of links to the words and deepen the students’ vocabulary knowledge inmind.However, the present vocabulary teaching approaches have proven to betime-consuming and ineffective (Lin, 2012). In the college,the decreasing of English classand increasing of the reading make more and more students feel the pressure of vocabularylearning. A lot of time and energy have been spent on vocabulary learning by the studentsbut they still complain that they cannot reach the mid-level, even to say the high and theyalso cannot avoid forgetting. Therefore, a large number of academic researchers andscholars have aimed at motivating the learners towards autonomous learning (Nunan 1995;Jiang 2006; Yao 2009; Yan 2010). However, these papers at home and abroad have probedinto the students’ autonomous learning method and process, and lacked of researches fromthe aspects of the role of the teacher.
………
1.2 Significance of the study
As the learners always complain the tedious of the vocabulary class and teacherscomplain that students don’t study hard, teachers should pay attention to teaching strategyand mode so as to change this vocabulary learning situation, such as time lost, lowefficiency, differential of effect on the vocabulary learning. Nowadays, an increasingnumber of people in China have paid attention to the teacher intervention of the classroomteaching, such as math teaching, music teaching and English distance teaching. No matterin which subject areas, as the classroom teaching is composed of three elements of teachers,students, teaching content, the teacher intervention will become the focus of attention.According to the Constructivism teacher intervention teaching mode, learners are notonly just to be passive stimulated and reaction, but also to be the proactive thinkers andproblem solvers. Language learners acquire knowledge, certain skills, strategies, andself-learning ability step by step. Ultimately, without the help of the teacher, the learnerswill reach a kind of level where they can learn independently and master the languageautonomously.While the constructivist teacher intervention vocabulary teaching mode makesteachers intervene more reasonably into the student’s study, instead of the full interventionof the traditional teacher in the vocabulary teaching, this is the subject of this paperresearch. It’s hoped this way of teaching will improve students’ vocabulary learningefficiency, and must make the research much more significant in the vocabulary teaching.
………
Chapter Two Literature review
2.1 Overview of teacher intervention
Systematic teacher intervention has been undertaken ever since teaching became aprofession. As early as in the nineteenth century, the structural view of language wasfounded by Saussure and promoted by Bloomfield (Zhao, 2011).Teacher intervention is used when dealing with a student who is having trouble inlearning a specific field. On the base of the structural view which limits knowing alanguage to knowing its structural rules and on behaviorism the traditional teacherintervention was aroused, which puts single emphasis on constant repetition andmechanical drills. Under the constructivist view of teacher intervention, effective teacherteaching approach intervenes in the students’ learning and applies in different waysaccording to the demands of specific situation. In addition, during a lesson or in a differentclassroom layout, the teacher’s role has to be changed.It is the first to know its definition for teachers to understand the constructivist teacherintervention. Thus in this part, it introduces the constructivist teacher, the definition ofconstructivist teacher intervention, the difference between constructivist teacherintervention and traditional teacher intervention and the researches on constructivistteacher intervention abroad and home.
………
2.2 A review of vocabulary teaching
As we all know, no matter in what languages, vocabulary is a very important part andwidely used all over the world. However, most teachers focus on grammar teaching orsome other abilities before 1990 in China. Until recent years, with the advent of variousability tests teachers have turned their attention to vocabulary teaching which rapidlybecome regarded as a basic task in the class. Vocabulary is getting more and moreattention. Obviously, productive knowledge requires more learning than receptive knowledge,that is to say, learners have to turn the simple word memory into particular or complicatedlexical knowledge for meeting their want. Wallace (1982) puts out nine criteria for test theability to know a word, first of all, the word’s written and spoken form should be known;second, without thinking the words can be blurt out; third, knowing its connotation andextension; fourth, mastering its deformation in different tenses; fifth, pronouncing in arecognizable way; sixth, spelling correctly; seventh, using correct collocation; eighth,using in appropriate occasion; ninth, being aware of its associations.Different kinds of knowledge require different kinds of teaching and learning, whichinvolve teaching vocabulary through listening, speaking, reading, and writing.
……..
Chapter Three Research methodology .... 20
3.1 Research questions ....... 20
3.2 Subjects ...... 21
3.3 Instruments of the study ..... 21
3.4 Procedure.... 24
Chapter Four Data analysis and discussion ........ 30
4.1. Analysis and discussion of tests .... 30
4.2 Analysis and discussion of questionnaires ....... 35
4.2.1 Analysis and discussion of pre-questionnaire..... 35
4.2.2 Analysis and discussion of post-questionnaire ......... 39
4.3 The Interview after the post-questionnaire ....... 44
Chapter 5 Conclusion........ 47
5.1 Major findings ........ 47
5.2 Implications of the study .... 48
5.3 Limitations and suggestions for further research ......... 49
Chapter Four Data analysis and discussion
4.1. Analysis and discussion of tests
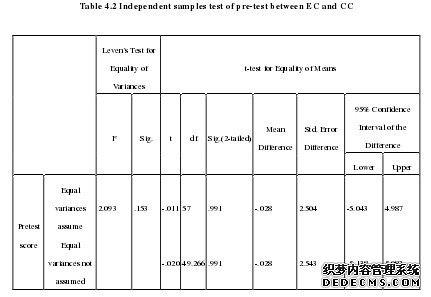
The pre-test carried out in the experimental class and the control class is to seewhether the students’ vocabulary level is roughly the same. The post-test in two classes isto check whether the vocabulary teaching model under the constructivist teacherintervention is positive in improving students’ vocabulary scores. Students’ scores arecollected from the pre-test and the post-test to compare if the experimental class and thecontrol class have statistically significant difference by the application of constructivistteacher intervention. The following data comes out from the SPSS will be analyzed indetail. As it vividly shows in the table of independent samples t-test, the Sig. value ofLeven’s Test for Equality of Variances is 0.153>0.05. It means the variance of the twoclasses is equal. Thus, the data in the line of Equal variances assumed are valid. Becausesig. (2-tailed) value is 0.991, which is more than 0.05, that is to say, there is no differencebetween the two classes. What’s more, 95% Confidence Interval of the Difference is from-5.043 to 4.987 with 0 existed. The data means there is no obvious difference between ECand CC again. It indicates that these two class students’ competence of vocabulary is nearlythe same. This is the premise of this thesis to launch the subsequent research. On thecontrary, if there is an obvious difference between the two classes, the result in post-testwill be meaningless. Therefore, it is practicable to choose the two classes to carry out thevocabulary teaching experiment.
……..
Conclusion
In this chapter, four parts will be written to conclude the thesis. The first part providesthe major findings of the study; the second part gives some implications for Englishvocabulary course; the third part presents the limitations and suggestions for furtherresearch will be put forward. Vocabulary is of vital importance in language learning and teaching. A task of boringand numerous words to remember are the most miserable thing which language learnersare facing when they study a foreign language every day. And language teachers are alsofacing the problem of assisting learners in storing and retrieving words and exploiting theirvocabulary learning efficiency. Vocabulary acquisition is a relatively gradual and longprogress including the acquisition of much more everyday used words and less commonones.This dissertation investigates the constructivist teacher intervention in college Englishvocabulary learning class. Firstly, in this study, the author tries to make a clear definition ofteacher intervention and better illustrates its significance and purpose to readers. Moreover,a four months experiment has been conducted to compare the difference betweentraditional teacher intervention and constructivist teacher intervention in collegevocabulary teaching. At last, based on the theoretical discussions and empirical findings, asuggestion to strike balance between the “spoon-feed” and “laissez-faire” teaching mode ismade, which is the constructivist view of teacher intervention teaching mode so that theirstrengths can be optimized.
…………
Reference (omitted)
