Chapter One Literature Review
1.1 Previous Studies on Language Ability Scale
Language Ability scale also known as language ability standard, is aseries of descriptions of the language users using certain language ability.Usually, each scale is divided several levels from low to high, used todescribe the different stages of the development of language ability. In theworld, the research on language ability scale has nearly 60 years ofhistory. The earliest language ability scale FSI is constituted by USAgovernment in 1955. Under its influence, a lot of language ability scalesappear in other area, for example, Australia's ISLPR scale, Canada's CLBscale, European ALTE scale, CEFR scale and so on. In recent years theChinese scholars also study on the language ability scale and achievemany results. FSI is used to test USA military and government sector expatriates'oral ability as a single skill scale. The indexes of statements in FSI scaleincludes accent, comprehension, fluency, grammar and vocabulary. Eachstatement index is divided into 6 main levels from 0 to 5 (equivalent tothe educated native holder) (Lucinda, 1994).The innovation of FSI scale lays on its first time to use a language todescribe the way to define personal oral communication ability in real life,which is the model for the following language ability to describe the scale(Han Baocheng, 2006). But the FSI scale is influenced by structurallinguistics, using the "skills + component" ability model as its foundation.The scale emphasizes that the mastery of language skills is to master thelanguage knowledge, but in fact the mastery of the language knowledge isnot necessarily to be used by learners.
……….
1.2 Previous Studies on Information Transferring Ability
In this section the previous study of information transferring abilityis introduced. As we know the research on information transferringability at home and abroad is a little few.Henry Widdowson (1973) officially quotes and introduces theconcept of information transferring ability in the "Applied Linguistics"magazine for the first time. He put forwards that non text information canbe accepted by people who speak different mother tongues in 1979, andthe non text information should be considered as a universal language ora part of it. More importantly, the non text information transferred intoEnglish written text information, or a non written form converted to the corresponding target language text, information transferring ability notonly challenges the target language output ability (oral or writtenexpression ability) of the second language acquisition, but also challengethe thinking mode.Li Li (2001) pointed out that the academic information we meetmight appear in the form of visual symbols rather than the pure languageform compared with previous time in teaching. Sometimes information inlist or symbolic form is easier to be accepted; sometimes information in avisual form and concise language will become easier to understand.Expressions of these two kinds of information can be considered asEnglish teachers giving students opportunities to exchange information.This kind of information conversion activity refers to the informationappearing as the visual symbol through students' recreation, namely theform converted from chart or diagram to pure text, or on the contrary.
……….
Chapter Two Theoretical Basis
2.1 Theory of Discourse Information Cognitive Processing Ability
The theory of Discourse Information Cognitive Processing Ability isa new theory, in this section, the development and the main contents ofthis theory will be introduced. The research methods of communicative language ability view andcognition ability view for language ability and cognitive process is theclassification. Classification is helpful to the understanding of languageability from the macro level, but the language understanding andexpression involve the integrated uses of various language ability andvarious psychological process, so only the classification is not enough, itneeds to use system theory, information theory and control theory, from system structure, information content and cognitive process three aspectsto investigate language ability. The main contents of discourseinformation cognitive processing ability include discourse informationcognitive processing system, cognitive processing ability, cognitiveproposition method for maximizing the quantitative calculation andinformation. Discourse information cognitive processing estimate the sizeof information according to the known and unknown content. Discourseinformation can be quantified in terms of content, and the key problem ishow to quantify. According to information theory, the information caneliminate the receiver's uncertain information on things, or new contentand new knowledge the receiver unknown; the amount of information isthe degree of removed uncertainty. Accordingly, the discourseinformation refers to some new— unknown content which is the carrier aslanguage and can remove the receiver's some uncertainty. (Deng Jie,2012).
………..
2.2 The Theory of Communicative Language Ability
The early language ability research takes Lado (1961) and Carroll(1968) as the representative. They put forward “Skills and Elements”language model (Purpura, 2008) on the influence of structural linguisticsand behavioral psychology. They believe that language ability is divisible,consisting of listening, speaking, reading, writing skills and pronunciation,vocabulary and grammar, “skills + components” model has greatinfluence on current language test development and research, whichcreates separation test, and makes a large-scale standardized language testbecome possible" (Wang Shuhua, 2012:9). Limitations of this model arethose: the first is "skill + component" model does not pay attention to theability of language interpretation, although it distinguishes the languageknowledge and language skills, but do not explain the relationship between them. The second is that it ignores the language learners ’ usescenarios (Bachman, 1990).
……….
Chapter Three Methodology........ 35
3.1 Research Design........ 35
3.1.1 Research Questions........ 35
3.1.2 Subjects........36
3.1.3 Instruments........38
3.2 Research Procedure........ 39
3.2.1 Data Collection ........40
3.3.2 Data Analysis........ 42
Chapter Four Results and Discussion........ 45
4.1 Construction of Information Transferring Ability Scale........ 45
4.1.1 Collection of "Can do" Statements of InformationTransferring Ability........ 45
4.1.2 Modification of "Can do" Statements of InformationTransferring Ability ........48
4.2 Validity of Information Transferring Ability Scale........ 49
4.2.1 Analytical Validation........ 50
4.2.2 Quantitative Validation........ 52
Chapter Four Results and Discussion
4.1 Construction of Information Transferring Ability Scale
The construction of information transferring ability scale includestwo steps, the one is to collect the "Can do" statements, the other is tomodify these statements. The "Can do" Statements of language ability is the basic operatinginstruments to describe language ability in language teaching and testing,namely, they are the basic standard terminology to describe language. Asystem of language ability statements is the embodiment of a certainlanguage ability theory, which provides the basic reference frame forlanguage teaching and testing in content.
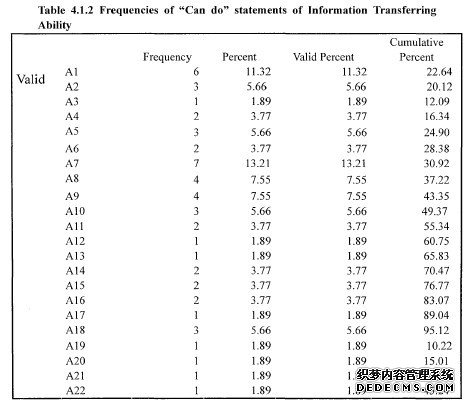
……….
Conclusion
So far, we have got the parameters and dimensionalities of "Can do"statements of information transferring ability and the common referencescale have been built. Based on the qualitative and quantitative analysisand the collected data on different section of this study, we can getrelatively objective answers to the research questions raised in chapterthree. Now, we will summarize the major findings and implications, andthen point out the limitations of the study.
…………
Reference (omitted)
