Chapter One Introduction
1.1 Research Background
At present, the cultivation of practical talents can't catch up with that of academictalents in China. The cultivation of practical talents just recently became a new major ofChinese higher education. As the outer inducement, the transform of needs in talents andthe unemployment of undergraduate caused by financial crisis leads the need of practicaltalents. With the development of Chinese social economy, the need of high level practicaltalents gradually intensifies to the entire society, but China mainly cultivates the highlevel of academic talents, which leads to the shortage of practical talents. Theemployment problem of undergraduate is related to the social politics and thedevelopment of higher education. While after the breaking out of global financial crisis in2008, the unemployment became more serious. As the inner inducement, it's about theneed of students' desire to promote self-competitiveness. Under the push of these twofactors, it is necessary to adapt to the urgent requirement of national social economicconstruction and social development, and to develop professional degree education withChinese characters. On March, 2009, Ministry of Education announced a paper namedNotification on Recruiting Full-time Professional Postgraduate Degree, and China beganto change the training mode of some professional postgraduate.
……..
1.2 Research Purpose and Significance
There are many researches on curriculum design, while the Full-time M.Ed is totallya brand new subject to be studied. The theoretical value of this research is: Firstly, it ishelpful to clarify the nature and characteristics of Full-time M.Ed; secondly, it helps toclarify theoretical connotation of Full-time M. Ed courses and curriculum setting,andprovides a theoretical basis for the reasonable construction and personnel training ofFull-time M.Ed courses. For a long time, the personnel training at postgraduate level ismainly academic type. But the development of applied talents is slow,resulting in unevenstructure of talent cultivation and the difficulty to meet the society demand for talent indifferent fields. For a long time, although the development of Master of Education degreehas got many achievements, but problems are still existed, such as the training way whichuses the reference from Master of Education. It does not highlight the occupational,applied and practical features of professional degree. The practical significance of thisstudy is:Firstly,this research meets the characteristics of the modem era, keeps pace with thedirection of economic development and China's educational development situation andnational education policy.
……..
Chapter Two Literature Review
2.1 Definition of Full-time M.Ed
Professional degree is a general title for those who are conferred with degreescompleted in M.Ed education other than arts literature and natural science, commonlyopposed to academic degree. A professional degree is often fiilfilled throu^out 2 or 4years in the fields of education, art,management and agriculture etc. It is accessible tohigher professional degrees, e.g. M.Ed in Education. The 1996's 14出 Plenary of StateAcademic Degrees Committee of the State Council reviewed and approved of the InterimProcedures in Professional Degree Designing as cited from the regulation as:"Professional degree is designed for special talents of higher levels in specific fieldsfeaturing certain occupational backdrop," "related industries to each professional degreeshall attribute in a gradual manner to one of conditional priorities concerningcorresponding occupational qualification,,. In 2002 the state circulated Strategic Reporton Chinese Degree and Postgraduate Education Development also entitles theprofessional degree as occupational degree,which is set up in some specific occupationalbackdrop. Most professional degrees overseas are associated with some occupationalqualifications to specific occupational fields.
………..
2.2 Definition of Curriculum
According to Gatawa( 1990:8), curriculum is “the totality of the experiences ofchildren for which schools are responsible". Tanner and Tanner define curriculum as “aplan or program of all experiences which the learner encounters under the direction of aschool,,(Tanner and Tanner 1995:158). Sergiovanni and Starrat (1988:258) considercurriculum as “that which the student is supposed to encounter, study, practice andmaster-in short the stuff of what the student leams”. In Beach and Reinhatz's (1989) view,a curriculum is a ‘‘prescribed series of courses to take".To sum up the definitions above, the curriculum is considered as a compositeincluding the learners, the teachers, teaching and learning methods, anticipated andunanticipated experiences, outputs and outcomes possible within a learning institution. There are three main views on curriculum setting: 1) Curriculum offered by schoolor other education institution; 2) The procedure of arranging teaching subjects accordingto teaching goals; 3) The parts of curriculum setting including curriculum types, teachingcontents, course structure, course period, curriculum forms and schedules.
……..
Chapter Three Research Methodology.......19
3.1 Research Content .......19
3.2 Research Participants....... 20
3.3 Research Methods....... 20
3.4 Data Collection............ 21
Charter Four Data Analysis....... 22
4.1 Basic Information....... 22
4.2 Expectation and Satisfaction....... 22
4.3 The Overall Impression of Students' View on the Curriculum....... 28
4.4 Students' Interview....... 35
Chapter Five Discussions on Full-time M.Ed....... 39
5.1 Setting a Systematical Guidance on Practicum....... 39
5.2 Keeping the Original Courses while Prolonging the Time Period....... 40
5.3 Emphasizing on Teaching Ability .......40
5.4 Renewing Teaching Materials on Time....... 41
5.5 Setting more Selective Courses Related to Teaching....... 41
5.6 Diversifying the Teaching Methodology .......42
5.7 Reconstructing the Curriculum .......43
Chapter Five Discussions on Full-time M.Ed
5.1 Setting a Systematical Guidance on Practicum
The rules of guidance, appraisal and evaluation on practicum should be clear. Aftergraduation, the direct job for professional graduates is Basic English Educator, whichrequires very strong ability to practice. Therefore, it is necessary to enhance the practicalability of students to put the learned theories into practice. Therefore, when teachingFull-time Masters of Education professional graduates, the teacher should arrange asmuch time as possible for undertaking practical teaching practices. In fact, theftindamental significance of teaching practices lies in the combination of theories andpractices, the converting of practical educational problems to scientific research problems,the improvement of scientific research ability of graduates, and the guiding role forpractical teaching. Therefore, it is better to follow foreign countries and to arrange acertain number of practice courses for every term to increase their experience and abilityon practical teaching and on practical research, such as educational survey, teachingobservation and simulation teaching. Moreover, establishing more definite standards forappraisal and evaluation for graduate students with regard to teaching practice isnecessary. Appraisal is an inspection as the results of teaching practice and evaluation isan analysis on the whole process of teaching practice.
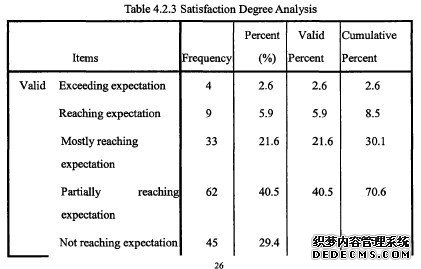
…….
Conclusion
Through studying the plans for developing graduate students in higher normalcolleges and universities that recruit Full-time Masters of Education, this paper hasundertaken a brief discussion on some problems existing in the course being set forFull-time Masters of Education.Most participants admit that they are partially satisfied with the cultivation program.This teacher education program is still not perfect. When it comes to the optimization ofthe program, those pre-service teachers hold the belief that there is much room for theimprovement such as the teaching materials,teaching methodology, teaching faculty,most importantly the curriculum and teaching practicum. They also complain about theimbalance among theoretical courses and practical courses,out-of-date teaching materialsand the traditional teachers-centered teaching methodology. Finally, some possible waysto improve the cultivation model are put forward.
…………
Reference (omitted)
