本文是一篇英语论文,本研究结果表明:(1)多模态话语分析理论下的词汇教学对学生的词汇学习策略有积极影响;(2)多模态话语分析理论下的词汇教学对学生的词汇成绩有积极作用。说明多模态教学在高中英语词汇教学中的应用是可行的,且积极有效。
Chapter One Introduction
1.1 Background of the Study
Vocabulary is the basic knowledge of a foreign language and the key to foreign language teaching. Many scholars have noticed the important role of words in English learning. Wilkins(1972) believed that if grammar was not used, it was difficult to express anything. But if there were no words, nothing could be said. In addition, McCarthy(1990) argued that it was impossible for words to be understood without a full understanding of semantics. Therefore, in English teaching, students must devote more energy to the vocabulary learning. Efficient learning of English words is the key to English learning, especially in senior high school. Therefore, efficient learning of English words has to be put on the agenda.
English Curriculum Standards (2017, revised in 2020) (2020) put out the specific requirements for English vocabulary. These requirements are to master 2,000 to 2,100 words used in practice for senior high school elective and compulsory courses; to cultivate and improve the ability of students to accurately comprehend and exactly express the meaning of vocabulary within contextual frameworks. Obviously, the new curriculum standards require students to pay more attention to their vocabulary. When reciting words, students should not only remember pronunciation and meaning, but also use words correctly in context. At the same time, students can use their own language to understand and express the concepts related to different topics. It can be seen from the requirements that students need better vocabulary learning strategies. Therefore, it is particularly important to carry out effective vocabulary teaching in senior high school English class.
1.2 Purpose and Significance of the Study
This part mainly describes the purpose of this study and the importance of conducting this study.
1.2.1 Purpose of the Study
In recent years, various advanced multimedia teaching methods have been widely used in domestic schools, which provides a feasible way for English teaching. Based on multimodal discourse analysis theory, this study intends to accomplish the following research objectives:
To explore the application of multimodal discourse analysis theory in English vocabulary teaching and its impact on students’ vocabulary learning strategies.
To explore the application of multimodal discourse analysis theory in English vocabulary teaching and its impact on student vocabulary learning outcomes.
Chapter Two Literature Review
2.1 English Vocabulary Teaching
This part defines the concept of English Vocabulary Teaching and introduces the recent researches abroad and at home.
2.1.1 Definition of English Vocabulary Teaching
In vocabulary learning, the first step is to understand its meaning, and deeply explore its grammatical structure and practical application methods, which constitute the core ideas of teachers to carry out vocabulary teaching. Vocabulary teaching should comprehensively cover the meaning, usage and related knowledge of vocabulary. Liu Ran(2018) emphasized that vocabulary teaching is not limited to the teaching of pronunciation and meaning, but should include the norms of morphology and practical exercises of words. Michael Lewis(1993) further elaborated that English vocabulary teaching consists of three steps: first, explain the meaning of words, then teach the characteristics of words such as conjugation, and finally teach students how to correctly use words in context. He advocated that vocabulary should be learned as a whole rather than memorized in isolation, which implied that vocabulary teaching should cover the collocation of phrases and fixed sentence patterns related to vocabulary.
Vocabulary is the cornerstone of language learning, and its lack of accumulation will greatly restrict learners’ language ability. The importance of vocabulary teaching in English is obvious. Vocabulary teaching is diverse, and each word interweaves and interacts with others in the vocabulary network to form a language system.
2.2 Multimodal Discourse Analysis Theory
This part defines the concept of multimodal discourse analysis and introduces the relevant studies on multimodal discourse analysis abroad and at home.
2.2.1 Definition of Multimodal Discourse Analysis
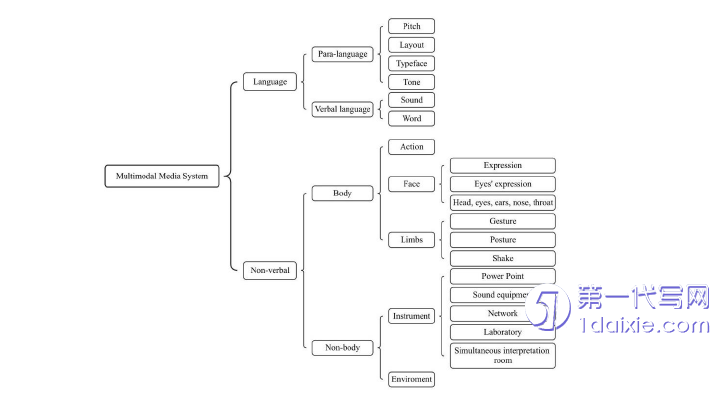
Multimodal discourse analysis refers to a phenomenon in which people use a variety of sensory modes to carry out social communication through different means and symbol systems in daily learning and life. This theory is based on the perspective of social semiotics and systematic functional linguistics. It emphasizes language as a social sign and constructs the whole meaning of society together with non-linguistic signs.
Jweitt(2006) emphasized that the reason for combining discourse with multimodality was that the expression in the real world was far more than the language itself, and other non-verbal content also played a key role in shaping the overall expression mode. Zhu Yongsheng(2007) pointed out that unimodal discourse relied on only one mode for expression, such as hearing news reports or visual appreciation of literary works. Multimodal discourse, on the other hand, is the fusion of different modes to play a role together. In daily life, people use two or more senses to communicate, thus forming a multimodal communication mode. Zhu Yongsheng further defines two dimensions of polymorphic discourse: one is from the modal type, which is regarded as a language form with multiple modes co-existing; Second, starting from the number of symbol resources, it emphasizes that a mode may contain many different symbols.
Chapter Three Theoretical Foundations ............................. 24
3.1 Social Semiotics ...................................... 24
3.2 Systemic Functional Linguistics................................. 25
Chapter Four Research Design .............................. 27
4.1 Research Questions ............................................... 27
4.2 Research Subjects ..................................... 27
Chapter Five Results and Discussion ........................... 39
5.1 Results and Discussion of the Results of the Teaching Experiment .......... 39
5.2 Results and Discussion of the Results of the Questionnaire ...................... 43
Chapter Five Results and Discussion
5.1 Results and Discussion of the Results of the Teaching Experiment
Vocabulary tests were conducted in both classes before and after the experiment, and the test scores were collected and organized, and descriptive statistical analysis and independent samples t-test were conducted on the test scores using SPSS20.0 data analysis software as a means of analyzing the changes in students’ vocabulary scores after applying multimodal teaching. All 115 students in both classes took the test, and the return rate of the test papers was 100%.
5.1.1 Results and Discussion of Pre-test Scores
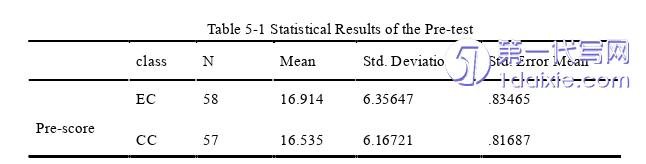
From the statistical results of the pre-test in Table 5-1, it can be seen that the average score of the test in the experimental class is 16.91, and that of the control class is 16.54. This indicates that the vocabulary level of the experimental class and the control class is basically the same before the experiment, and there is not a big difference between them.
Chapter Six Conclusion
6.1 Main Findings
Through the investigation and research, it was found that the use of multi-sensory, multimodal symbols from the use of text, animation video, sound, PPT, and the use of the Internet to teach English vocabulary activities to students greatly increased the students’ enthusiasm for vocabulary learning and strengthened their confidence in learning English vocabulary.
Firstly, the application of the multimodal vocabulary teaching method favorably influences the utilization of vocabulary learning strategies among senior high school students, particularly those about associative and contextual techniques. Furthermore, this teaching method has a positive impact on the use of metacognitive strategies among students. As evidenced by the questionnaire’s results, the multimodal approach, in contrast to the traditional vocabulary teaching model, effectively enhances students’ capacity to enhance planning awareness and monitor their learning progress during vocabulary acquisition, thereby enabling prompt adjustments. It can help students choose appropriate learning methods according to various vocabulary items. Accordingly, the multimodal vocabulary teaching approach facilitates students’ effective utilization of metacognitive strategies, thereby enhancing their autonomous learning capabilities. Furthermore, the multimodal vocabulary teaching mode exerts a beneficial influence on high school students’ employment of cognitive strategies. The questionnaire’s revelations indicate that within the framework of the multimodal vocabulary teaching method, teachers employ multimedia instruments and multimodal resources to aid students in constructing the meaning of vocabulary, thereby reducing rote memorization and frequent dictionary consultation. The results of the questionnaire survey show that students’ use of associative and contextual learning strategies increased significantly under the multimodal vocabulary teaching model, from 14% before the experiment to 70% in the end.
reference(omitted)
