本文是一篇英语论文,本研究结果表明:(1)学生在文章结构、关键信息提取、作者写作意图等方面的解读有所提升。(2)学生的阅读成绩有一定的提高,并且学生在阅读中还掌握了一些阅读技巧。
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Background of the Study
The information age brings people all kinds of convenience and also puts forward new challenges to people: to keep pace with times. It is necessary to improve one’s abilities to obtain information, among which reading ability is the most important one. It is becoming more and more important to improve English reading ability. English reading, which occupies an important position in English language acquisition, is the main source for students to acquire information. It’s also an important guarantee for learning English well and an effective means to improve English performance. The level of reading ability also determines, to a certain extent, a student’s written expression ability and oral communication ability. In senior high school English teaching, although teachers attach great importance to reading teaching and students spend a lot of time and energy in reading, the effect is not proportional to the effort. Kuai Lei (2016) has pointed out that the current English reading teaching pays too much attention to sentence grammar and vocabulary learning, thus ignoring the process of discourse processing and comprehension. Zhang Meijun (2020) believes that the use of the traditional rigid English reading teaching mode, for lack of consideration from the students’ point of view, makes the teacher dominating the reading classroom, resulting in a comparative lack of active motivation in students’ learning, which affects the efficiency of students’ English reading. In order to solve the current problem in English reading classroom teaching, Zhong Min (2020) puts forward an opinion that teachers should combine the discourse context, input cultural background knowledge to stimulate students’ background schema, combine macro-analysis and micro-analysis to cultivate students’ overall skills, reasonably choose the textbook discourse, adjust the form of the reading questions, and improve the standard of reading ability measurement.

1.2 Purpose of the Study
Reading teaching plays an important role in senior high school English reading. According to new Curriculum Standards and the current state of English reading teaching, incorporating discourse analysis into senior high school English teaching has been implemented in order to enhance teaching practices and further develop discourse analysis theory under the situation of evolving college entrance examination format. The main purpose of this study is to investigate a new approach to senior high English reading teaching and to determine, through research and experimental teaching, whether the implementation of discourse analysis in senior high school English reading teaching can change students’ reading behavior. This study confirms that to improve students’ reading level, they must not only be able to consciously analyze the genre of an article, understand its structure, and summarize its main idea using discourse macro means, but also apply discourse micro means in the process to learn vocabulary, sentence patterns, and grammar simultaneously. Meanwhile, reading comprehension accounts for a great proportion of the score in the English college entrance examination. However, due to the time and type of examination limitations, students can complete five reading passages within the limited time only by mastering the word and phrase method. It is far from enough that students need to understand the material from the perspective of discourse, master the discourse framework and author’s writing intention, simply by analyzing words, phrases and sentences.
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 Discourse and Discourse Analysis
This part discusses the definition of discourse and discourse analysis in detail.
2.1.1 Definition of Discourse
Harris (1952) defined discourse as coherent spoken or written language. Van Dijk’s (1997) point of view was that discourse was based on social contexts, with language acting as a medium to realize the exchange of ideas. Hu Zhuanglin (1998) pointed out that discourse was based on context to express meaning. Liu Chentan (1999) believed that as a linguistic unit, the use of discourse was not abstract, fragmented or random. McCarthy and Carter concluded that language was discourse (Cheng Xiaotang, 2005). According to Huang Guowen and Ge Dasi (2006), discourse was a unit of language use and semantic unit. Zhang Yinglin (2006) defined discourse as language used in situational, social, cultural and psychological contexts. Lin Wei and Yang Yuchen (2007) concluded that discourse should cover both oral and written products of communication. Xi Xiaoqing (2011) believed that all segments of speech that could function in a certain context or carry out a certain function could be regarded as discourse. Widdowson (2012) pointed out that discourse was the combination of the author’s intention in the text and the reader’s meaning in the text. Widdowson also believed that discourse was the use of combined sentences.
2.2 Current Research on English Reading Teaching
Reading is a crucial avenue for the successful acquisition of knowledge and language input, with an abundance of reading enhancing English’s comprehensive capacity. A lot of research focuses on English reading teaching. These studies mainly cover the model, subjects, importance of English reading teaching and the interaction of English reading. These studies have broadened horizons to understand the current research on English reading teaching.
The model of English reading teaching: There were three models to English reading teaching. The first one was the Top-Down Model, as proposed by Goodman (1967), which focused on utilizing prior knowledge and experience to actively engage in the reading process by guessing, testing, revising, and re-guessing until comprehension is achieved. The second one was that Gough (1972) introduced the Bottom-Up Model, where reading began with decoding individual words and progresses through sentences and paragraphs towards a greater understanding of the text. The third one was that Rumelhart (1977) proposed the Interactive-Reading Model, a hybrid of Top-Down and Bottom-Up approaches that emphasized the reader’s interaction with the material they are reading. Rather than passively absorbing the information, the reader was able to construct it from their own original understanding. This combination of two methods of reading effectively revealed the cognitive process of reading.
Chapter 3 Research Methodology .............................22
3.1 Research Questions ...................................22
3.2 Research Design .........................................22
Chapter 4 Results and Discussion ..............................40
4.1 Data Analysis .......................................40
4.1.1 Data Analysis of Questionnaire ..........................40
4.1.2 Data Analysis of Pre-test and Post-test ...........................44
Chapter 5 Conclusion .....................................61
5.1 Major Findings. ..........................................61
5.2 Pedagogical Implications .........................63
Chapter 4 Results and Discussion
4.1 Data Analysis
Before and after the experiment, data analysis were conducted in CC and EC. So this part was composed of analysis of questionnaire, pre-test and post-test and interview.
4.1.1 Data Analysis of Questionnaire
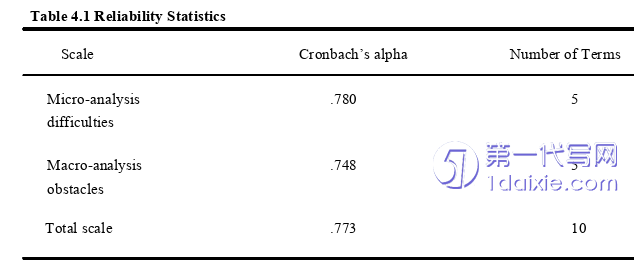
At the beginning of the experiment, in order to better understand what the effect of senior high school English reading teaching based on discourse analysis on students’ ability to interpret discourse texts was, a questionnaire was designed for senior high school students, with a total of 10 questions divided into two dimensions. The first five questions were difficulties related to discourse micro-analysis, such as word meaning guessing, sentence, grammar, and cohesion and so on. The last five questions were obstacles related to macro-comprehension of the discourse, such as reasoning judgment, writing intention, the clue of the text and the general idea. The distribution of questionnaire was conducted at the beginning of the first semester and at the end of the first semester of the 2023-2024 academic year. Fifty questionnaires were distributed and all of them were taken back. Finally, the data from the returned questionnaire are analyzed by using SPSS21.0 and the results are as follows.
Chapter 5 Conclusion
5.1 Major Findings.
As is indicated previously, all the data and results of questionnaire, tests and interview are concluded as major findings in the study to seek answers to three questions.
(1) Students’ interpretation of the structure of the text, extraction of key information, and author’s writing intention is improved.
The analysis of questionnaire survey shows that discourse analysis teaching can strengthen students’ discourse text interpretation ability in the following aspects: 1) Helping students understand the structure of the text: It can be seen that reading teaching method based on discourse analysis can help students reduce the difficulties and obstacles in reading comprehension to a certain extent. 2) Guiding students to grasp key information: Students tend to understand the text from a whole, rather than translate it word by word, sentence by sentence. Through discourse analysis, students can learn how to grasp the key information in a text, sort out the main points and details of the text, and obtain the main points and detailed information of the text effectively. 3) Enhancing students’ reading skills: It can be concluded that students can learn various reading skills, such as predicting, inferring, summarizing, which will help them read and comprehend texts more efficiently. 4) Expanding students’ vocabulary and grammar knowledge: It can be concluded that discourse analysis can help students learn vocabulary and grammar knowledge in specific contexts and improve their language expression. In short, discourse analysis is very important in senior high school English reading teaching, which helps students better understand and interpret the content of the text.
reference(omitted)
