本文是一篇英语论文,本研究采用实验法,以广东省梅州市某中学高二年级两个平行班的105名学生为研究对象进行实验研究。
Chapter One Introduction
1.1 Research Background
Vocabulary learning plays a crucial role in the development of language skills(Schmitt,2008).Any language skills such as listening,speaking,reading,writing,andtranslating are closely related to vocabulary.Therefore,vocabulary acquisition is acentral task of second language acquisition(Lewis,1993).General Senior HighSchool Curriculum Standards(English)(2020)has set specific vocabularyrequirements for senior high school students.At the stage of the required courses,students are required to master 2000 words in total,including 1500 words that theyhave learned at the compulsory education stage.Besides,senior high school studentsshould be able to use 1000 additional new words after learning the required electivecourses,with an accumulative total of 3000 words.In addition,General Senior HighSchool Curriculum Standards(English)(2020)has put forward specific requirementsfor English vocabulary teaching in senior high schools,that is,vocabulary teachingshould aim at a higher level of depth and width in using vocabulary and focus onfurther expanding students’vocabulary through extensive reading so as to enhancetheir ability to understand and express meaning more accurately.Based on the above,English teachers in senior high schools should attach great importance to vocabularyteaching.
1.2 Research Objectives
Vocabulary is as important to language as bricks are to a whole building.Atpresent,numerous studies have shown that IVA can be effectively achieved by settingintervention tasks such as reading plus activities,and the output task is one of theintervention tasks.Guided by the Output Hypothesis(Swain,1985)and theInvolvement Load Hypothesis(Laufer&Hulstijn,2001),this study aims to explorewhich reading-based output task,sentence translation or sentence writing,has bettereffects on incidental English vocabulary acquisition of senior high school students,and to compare the effects of these two output tasks on the incidental Englishvocabulary acquisition of senior high school students at different English proficiencylevels,so as to provide implications for English vocabulary teaching and learning insenior high school.
Chapter Two Literature Review
2.1 Core Concepts
In this section,two core concepts are introduced in order to have acomprehensive understanding of them and lay a foundation for this study.These twoconcepts are output task and IVA.
2.1.1 Definition of output task
Ellis(1994:295)defines output as“language produced by learners”.Swain,whoproposed the Output Hypothesis,does not give a clear conceptual definition of output.In her articles,she only gives synonyms with similar meanings,such as“producinglanguage”(Swain,1995:125),“language performance”,“using the language”,and“speaking or writing”(Swain,1995:127),and“production or use”(Swain&Lapkin,1995).In Swain’s view,the term output is dynamic.It is not only the language thatlearners produce,but also the task that learners perform to produce the language.According to the Longman Dictionary of Language Teaching and Applied Linguistics(2010),output refers to“language produced by a language learner,either in speech orwriting”.In addition to speaking and writing,some scholars believe that output alsoincludes translation.Laufer and Girsai(2008)and Huang(2008)hold the view thattranslation is essentially a kind of pushed output.Wen(2008)proposes in the contextof foreign language teaching in China that output also includes interpreting andtranslating(from Chinese to English and from English to Chinese).Therefore,it canbe concluded from the above definitions that output refers to the language producedby language learners either in oral or written form,which includes speaking,writing,interpreting,and translating.
2.2 Previous Research on IVA
The study of IVA has gone through a long period of time from its inception,emergence and development to its maturity.Since the 21st century,the field ofincidental second language vocabulary acquisition has undergone a developmentprocess from slow growth to fluctuating growth,and then to rapid growth(Yang&Luo,2022).This section reviews the literature on IVA at home and abroad.
2.2.1 Previous research on IVA abroad
Nagy et al.(1985)introduced the concept of IVA on the basis of studyingchildren’s vocabulary learning of their native language.They argued that most of thenative vocabulary is likely to be acquired incidentally,but not by intentional learning.Since this is the case with native language vocabulary acquisition,what is the casewith second language vocabulary acquisition?Is it possible that most second languagevocabulary can be acquired through incidental learning?To this end,many scholarshave made studies on IVA.Generally speaking,a certain degree of IVA occursalongside the development of other language skills(Gai,2003a).In the following,theauthor introduces the related studies of IVA abroad from four aspects:listening,speaking,writing,and reading.
Chapter Three Theoretical Framework ................................. 22
3.1 Output Hypothesis ............................................ 22
3.1.1 Introduction to the Output Hypothesis ................................ 22
3.1.2 Application of the Output Hypothesis to the present study ....... 24
Chapter Four Methodology ................................. 29
4.1 Research Questions .................................. 29
4.2 Research Subjects ........................................... 29
4.3 Research Materials ........................................ 30
Chapter Five Results and Discussion ................................. 45
5.1 Results ....................................... 45
5.1.1 Effects of two reading-based output tasks on IVA of senior high school students ................... 45
5.1.2 Effects of two reading-based output tasks on IVA of senior high school students at different English proficiency levels ............. 48
Chapter Five Results and Discussion
5.1 Results
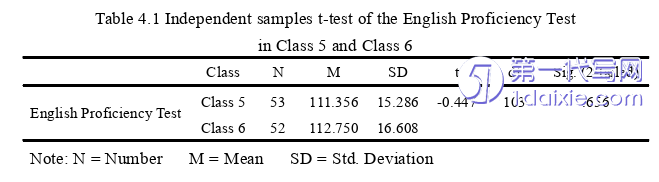
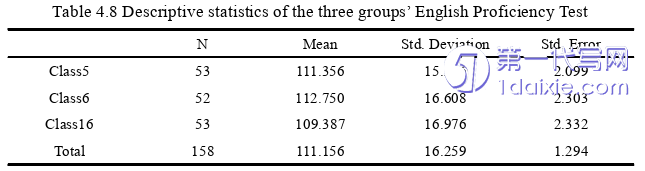
The objective of this study is to compare the effects of two reading-based outputtasks,namely the sentence translation task and the sentence writing task,on theincidental English vocabulary acquisition of senior high school students,and furthercompare their effects on the incidental English vocabulary acquisition of senior highschool students at different English proficiency levels.Therefore,the results of theimmediate and delayed vocabulary post-tests in the two rounds of experiments aredescribed and analyzed in the following sections.
5.1.1 Effects of two reading-based output tasks on IVA of senior high schoolstudents
In this study,research question one attempts to compare the effects of tworeading-based output tasks,namely sentence translation and sentence writing,on theincidental English vocabulary acquisition of senior high school students.Therefore,the data of the immediate vocabulary post-tests and the delayed vocabulary post-testsof the subjects in the two rounds of experiments were put into SPSS 18.0 fordescriptive analysis and the independent samples t-test.The specific results are asfollows.
Chapter Six Conclusion
6.1 Major Findings
Based on previous studies on IVA at home and abroad,and guided by the OutputHypothesis and the Involvement Load Hypothesis,this study mainly adopts theexperimental method to compare the effects of two reading-based output tasks,namely the sentence writing task and the sentence translation task,on the incidentalEnglish vocabulary acquisition of senior high school students,and further comparetheir effects on the incidental English vocabulary acquisition of senior high schoolstudents at different English proficiency levels.According to the data and discussionin Chapter Five,the following major findings are made in this study:
Firstly,the analysis of the data from the two rounds of the immediate anddelayed vocabulary tests shows that students in the sentence writing group and thesentence translation group have acquired the target words incidentally to some extent.That is to say,both the sentence translation task and the sentence writing task canfacilitate incidental English vocabulary acquisition of senior high school students tovarious degrees.This finding is in line with Bao’s(2015)finding that both thesentence translation output task and the sentence writing output task are effective infacilitating the incidental acquisition of English vocabulary,which further proves theimportance of output tasks in incidental English vocabulary acquisition.
Secondly,the performance of the sentence writing group is significantly betterthan that of the sentence translation group in the two rounds of the immediate anddelayed vocabulary tests.This shows that the effect of the sentence writing task issignificantly better than the sentence translation task in facilitating the incidental Secondly,the performance of the sentence writing group is significantly betterthan that of the sentence translation group in the two rounds of the immediate anddelayed vocabulary tests.This shows that the effect of the sentence writing task issignificantly better than the sentence translation task in facilitating the incidental
reference(omitted)
