本文是一篇英语论文,笔者认为在语言能力方面,学生的词汇知识和阅读能力处于较高水平和理想水平,而语音、语法和文本知识以及阅读和写作技能处于中等水平,需要提高;遗憾的是,学生的话语知识和口语技能水平较低,亟待关注。
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Background of the Study
In December 1997, the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) launched the project called “Definition and Selection of Competencies: Theoretical and Conceptual Foundations (DeSeCo)”, initiating research on key competency. After years of discussion and research, OECD published its final research report Key Competencies for a Successful Life and a Well-Functioning Society in 2003, which caused a huge response. Subsequently, international organizations such as UNESCO, the European Union, and the United States, the United Kingdom, Japan and other different countries have successively carried out research and construction on the key competency framework. The world's attention to education has converted from the former focus on knowledge to focus on students' ability development and quality cultivation.
In March 2014, the Ministry of Education of China (MOE) issued the Opinions on Comprehensively Deepening Curriculum Reform and Implementing the Fundamental Tasks of Building Morality and Cultivating People (referred to as the Opinions), in which the idea of key competency was first proposed. In September 2016, the Key Competency of Chinese Students’ Development was officially released in Beijing, which established the overall framework of student key competency with “fostering well-rounded people” as the core. In December 2017, the General High School English Curriculum Standard (2017 Edition) (referred to as Curriculum Standard 2017) was officially issued, which means that the English curriculum reform has entered a new era of “key competency”. The objective of the English subject curriculum converts from fostering students’ overall language ability to fostering their English key competency.
1.2 Purpose of the Study
The development of English education is pushed forward by English key competency, and the reform of education and teaching is also faced with many opportunities and severe challenges. Meanwhile, it also puts forward more stringent requirements for front-line English teachers and students. In our country, classroom teaching is the main position to cultivate students’ English key competency, and it is a long-term and arduous task to implement the English key competency in senior high school English teaching. The purpose of this study is to find out the main factors that affect the effective cultivation of high school English key competency by investigating the current situation of English key competency cultivation in the target schools, and get inspiration from it to promote the better implementation of English key competency in high school English teaching.
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 Definitions of Core Concepts
2.1.1 Key competency
“Key competency” is also called “21st century competencies” or “21st century skills” (Zhang, 2016). In December 1997, OECD launched the project called DeSeCo, which initiated research on key competency. After several years of hard practice, discussion and research, OECD published the ultimate research report that shocked the academic community in 2003. The name of the report is Core Literacies for a Successful Life and a Sound Society, which caused a huge response (Rychen & Salganik, 2003). Deseco project team defined the connotation of key competency: key competency refers to the important competency covering multiple life fields, promoting successful life and healthy society (Zhang, 2013). In 2005, the European Union published the Key Competency of Lifelong Learning: European Framework of Reference, which states that key competency has three levels: the first level is the accomplishment of self-realization and development, the second level is the accomplishment that social individuals can become active citizens, and the last level is the accomplishment of social people's integration into society and successful employment. (Gordon, 2009).
Cai Qingtian, Chu Hongqi and Lin Chongde are representatives of the definition of key competency in China. Cai (2012) thinks that “key competency is the necessary literacy that individuals in social groups should learn together”, Chu (2016) thinks that key competency is key quality that everyone should have so as to deal with the social change and development in the 21st century, Zhang (2016) thinks that “key competency is the development and transcendence of basic skills in agriculture and industry, and its core is the ability of creative thinking and complex communication”, Based on the analysis and comparison of the definition of key competency in the three major organizations and various countries in the world, combined with the practical needs of China’s basic education reform, Lin (2016:29) defined key competency as “during the process of accepting the corresponding period of education, students gradually form the necessary character and key ability to meet the needs of personal lifelong development and social development”.
2.2 Theoretical Basis
2.2.1 Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives
The teaching plan design first is to determine the educational goal. Therefore, the accurate classification of educational objectives is of great significance. Among the numerous theories of educational goal classification, Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives is very representative, which has important reference value for teachers to analyze and design teaching objectives.
In 1948, the idea of educational goal classification system was presented at the annual conference of psychology in Boston by a group of test experts. Bloom and D.R. Krathwohl are the main representatives. Bloom and others separated the educational goals into three areas: the first area is cognitive domain, affective domain is the second area, and the third area is psychomotor domain. The classification of educational objectives mainly focuses on two aspects: one is to guide the teaching process, the other is to evaluate the teaching results, so it essentially belongs to a classification of teaching objectives. In 1956, Bloom and others published The Taxonomy of Educational Goals, Volume 1: Cognitive Domain, which divides the goals of cognitive domain into six sub domains. The first is knowledge, the second is comprehension, application is regarded as the third, the fourth is analysis, the fifth is synthesis and the last one is evaluation. Aside from the application category, different subcategories are contained by the other five categories. Theoretically, these categories can be arranged in two ways, one from simple to complex goals, and the other from concrete to abstract goals, both of which emphasize the concept of cumulative hierarchy. From the perspective of teaching, the six categories have higher and higher requirements for students. In fact, since the theory was put forward, different countries have applied it to the guide of setting teaching objectives in teaching, among which the most frequent application is to apply it to the classification of curriculum objectives and test items (Wu, 2018).
Chapter 3 Methodology ............................... 26
3.1 Research Questions ........................... 26
3.2 Research Participants ..................................... 26
3.3 Research Instruments ............................... 27
Chapter 4 Results and Discussion .......................... 32
4.1 Results and Discussion of Students’ Questionnaire ............................ 32
4.1.1 The current situation of students’ language ability ................. 32
4.1.2 The current situation of students’ cultural awareness ............. 34
Chapter 5 Conclusion .................................. 60
5.1 Major Findings ................................ 60
5.1.1 Current situation of cultivating students’ English key competency................................. 60
5.1.2 Factors affecting the cultivation of students’ English key competency................. 61
Chapter 4 Results and Discussion
4.1 Results and Discussion of Students’ Questionnaire
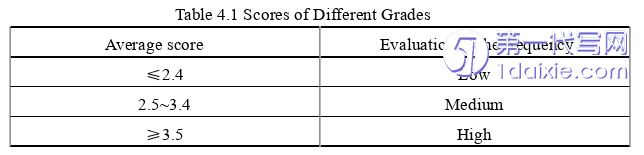
In the Five-point Likert Scale, strongly disagree = 1 point, disagree = 2 points, uncertain = 3 points, agree = 4 points, strongly agree = 5 points. If the average score is equal to or higher than 3.5, it is high-frequency use, if it is between 2.5 and 3.4, it is medium use, and if it is equal to or lower than 2.4, it is low-frequency use (Oxford & Burry, 1995), which is as shown in Table 4.1.
4.1.1 The current situation of students’ language ability
In Curriculum Standard 2017, the “language ability” of students at all stages is scientifically defined. At present, the main goal of senior high school English in China is to foster students’ mastery of language knowledge and improve their ability. Language ability is the foundation of English key competency. Whether it is the formation of students’ cultural awareness, the development of thinking quality, or the acquisition of learning ability, the achievement of three goals is inseparable from the support of language ability. Therefore, the investigation on the cultivation of students’ language ability is carried out.
Chapter 5 Conclusion
5.1 Major Findings
5.1.1 Current situation of cultivating students’ English key competency
Generally speaking, the cultivation of students’ English key competency in Lianyungang is not ideal, and the development of its four literacies is unbalanced. The development of cultural awareness is the best of the four literacies, followed by the development of students' language ability and learning ability, while the development of thinking quality is the worst, and the development of various abilities contained in each literacy is also uneven.
In terms of language ability, students’ vocabulary knowledge and reading ability are at a high level and ideal, while their phonetic, grammatical and textual knowledge and reading and writing skills are at a medium level and need to be improved; Unfortunately, students’ discourse knowledge and speaking skills are at a low level and need to be paid attention to urgently.
In terms of cultural awareness, it is the best among the four objectives of English key competency. Cultural awareness includes five aspects, such as cultural acquisition and so on. Students are at a high level in cultural understanding and cultural values, which is relatively satisfactory; Students’ performance in cultural acquisition and comparison of cultural similarities and differences is at a medium level, and there is room for improvement; In cross-cultural communication, students’ performance is at a low level and needs to be paid more attention.
reference(omitted)
