本文是一篇英语毕业论文,本研究遵循“计划—行动—观察—反思”的行动研究过程,在读前、读中、读后环节分别设置教学活动来调动学生多种感官的融合。通过问卷调查、测试卷、访谈以及课堂观察等多种研究工具收集数据,并借助SPSS26.0软件对其进行统计分析。
Chapter One Introduction
1.1 Research Background
English reading is a fundamental skill in English learning, and it is of great importance to English learning. On one hand, learners can increase their vocabulary, improve their writing ability and develop comprehensive English skills through reading (Wang Jing, 2005). On the other hand, The English Curriculum Standards for Senior High School (2017) points out that students can be proficient in the application of language after absorbing a certain amount of language materials and conducting a certain amount of language practice, which needs to be achieved through English reading teaching. It can be seen that reading is an effective way to promote English learning, and the importance of English reading teaching is self-evident.
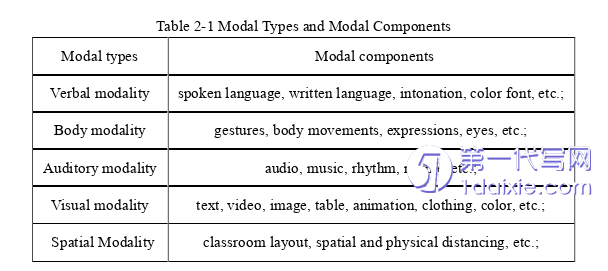
The rapid development of modern science and technology has changed the way information is disseminated and exchanged, providing more possibilities for the use of informatization and digital technology to innovate teaching mode and learning methods. In high school English teaching, teachers should provide students with more opportunities to learn and use language, encourage them to participate in the classroom actively to explore and discover the rules of the language, and formulate good learning strategies to cultivate students’ independent learning ability. At the same time, in the process of language teaching, teachers should creatively develop and make use of English learning resources, and actively use audio, video, radio, television, books, magazines, and Internet information to enrich the content and form of English teaching and expand the ways students learn and use English. The English Curriculum Standard for General Senior Secondary Schools (2017 edition) proposes 16 criteria for reading comprehension skills in the compulsory course, including: comprehending the meanings conveyed by non-textual resources such as pictures, images, sounds, symbols, colors, and so on, in multimodal discourse (e.g., films, TV, posters, songs, and comics).
1.2 Research Purpose
In view of the importance of English reading and some of the problems existing in the current English reading teaching, it is believed that it is very important to change the traditional English reading teaching method that is dominated by teacher, and improve students’ reading motivation and reading level. Reading motivation can stimulate students’ interest and enthusiasm for reading and enhance students’ concentration. In addition, reading motivation can also improve students’ language expression skills, critical thinking and analytical skills. This study aims to apply multimodal teaching to English reading teaching, so as to make students feel the pleasure of reading through the mobilization of multiple senses, and then to stimulate students’ reading motivation and improve their scores in reading. In addition, it is hoped that the application of multimodal teaching can provide new teaching strategies and ideas for high school English teachers, and provide suggestions and references for the implementation of reading teaching in high school English classroom.
Chapter Two Literature Review
2.1 Core Concepts
This part expounds the core concepts of this research, including multimodality, multimodal teaching and reading motivation.
2.1.1 Multimodality
2.1.1.1 Definition of Multimodality
In the early 1990s, there was a surge of research on multimodality in foreign countries, and it has gradually gained the attention of the linguistic community. Different scholars have different views on multimodality. Halliday (1978) first defined multimodality. He thought that people use a variety of symbols and resources to convey meaning in interpersonal communication, and the different information expressed by these symbols is output and expressed in a comprehensive form, and this systematic pattern is called multimodality. Kress & Van Leeuwen (2006) considered the simultaneous use of multiple modalities as multimodality. They stated that multimodality is the mode and manner of information exchange between a person and the external environment with the help of some intermediators. Gu Yanguo (2007) believed that modality is the mutual perception between people and the external environment by using multiple senses. It includes the communication of other symbol systems such as words, hearing, colors, etc. Unimodal refers to the role of a single sense, while multimodality refers to the process of interaction between multiple senses. Zhu Yongsheng (2007) regarded multimodality as the medium and communication channel through which people communicate.
2.2 Theoretical Basis
2.2.1 Multimodal Discourse Analysis Theory
In the 1990s, linguists Kress & Van Leeuwen proposed the theory of multimodal discourse analysis. Traditional theories usually take language as a single social symbol for theoretical analysis and functional meaning research, while multimodal discourse analysis theory focuses on other symbolic systems besides language, and at the same time emphasizes the independence and relevance of these symbols, so as to analyze and integrate the characteristics of language. The theory focuses on the role and function of non-traditional language symbols such as images, colors, movements and sounds in the expression and transmission of discourses.
Based on Halliday’s understanding of the framework of Systemic Functional Linguistics, Zhang Delu (2015) constructed a theoretical framework for multimodal discourse analysis, which consists of four dimensions: the cultural dimension, the contextual dimension, the content dimension, and the expressive dimension. The most crucial of the four dimensions is the cultural dimension, which determines the traditions, forms, and techniques of communication. This dimension includes ideology, thinking mode, living habits and other ideologies, which is the foundation of the whole communication system, determines the forms and techniques of people’s communication, and is also the key dimension to make multimodal communication from abstract to concrete. At the contextual dimension, while the communication is constrained by contextual factors such as the tone of discourse, and the mode of discourse, the genre of choice should be carried out in communication. The content dimension consists of meaning and form. The meaning dimension refers to discourse meaning, consisting of conceptual, interpersonal and discourse meanings. The formal level refers to the lexicogrammar, including verbal, graphic, image and sensory. At this dimension, the formal features of different modalities are interrelated. The expressive dimension refers to the media level, including linguistic patterns and non-linguistic modes.
Chapter Three Research Design.............................. 18
3.1 Research Questions ............................ 18
3.2 Research Subjects ............................... 18
3.3 Research Instruments ........................... 19
Chapter Four The Process of Action ........................................ 28
4.1 The Preparation for Action Research ..................... 28
4.2 The First Round of Action Research ............................. 32
4.3 The Second Round of Action Research ............................... 46
Chapter Five Data Analysis and Discussion ................................ 64
5.1 Results of the Questionnaire .................... 64
5.2 Results of English Reading Tests ..................... 68
5.3 Results of the Interviews .................................. 69
Chapter Five Data Analysis and Discussion
5.1 Results of the Questionnaire
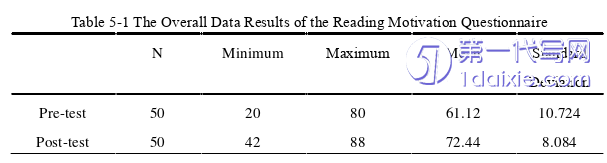
In order to explore the effect of the application of multimodal teaching in high school English reading teaching on students’ reading motivation, this research adopts a quantitative analysis method and imports the data results of the reading motivation questionnaire before and after the action research into SPSS26.0 software to compare the results of the pre-test and the post-test.
5.1.1 The Overall Data Analysis of the Questionnaire
In order to know the changes of students’ reading motivation before and after the action research as a whole, the researcher imports the pre- and post-tests data obtained from the high school students’ reading motivation questionnaire into SPSS26.0 for analysis. In order to clearly show the change, this paper only presents the important data in the table. The results are shown in the following table.
Chapter Six Conclusion
6.1 Major Findings
Based on extensive literature review and two rounds of action research, this research aims to explore the effect of the application of multimodal teaching in high school English reading teaching on students’ reading motivation and scores in reading tests. According to research questions, the researcher uses research instruments, such as the questionnaires, test papers, interviews, and classroom observation scales, and summarizes the main findings based on the analysis of the results.
First, after the 16 weeks action research, students’ reading motivation improves significantly overall after the implantation of multimodal reading teaching, and the degrees of improvement in each dimension are diverse. Among them, the intrinsic motivation of reading is the most improved, followed by sense of self-efficacy, and the social interaction motivation and extrinsic motivation are relatively weak. Multimodal teaching uses the cooperation of verbal, body, visual, auditory, spatial and other modalities to stimulate students’ multiple senses and provides students with rich learning resources, ideal learning environment, good reading habits and efficient learning strategies, which can attract students’ interest and improve students’ participation in the classroom. It can be found that after the application of multimodal teaching, students are more interested in reading, more willing to take the initiative to read and communicate with others, and have a higher self-confidence and a sense of achievement. In the classroom, the teacher transforms boring text into pictures, videos, audios, tables, mind maps, etc., which makes abstract content became concrete and reduces the difficulty of reading articles.
reference(omitted)
