本文是一篇英语毕业论文,本文不仅是对奈达翻译理论应用的扩充,也是对外宣英译的新实践。奈达翻译理论与外宣翻译的结合不仅能准确地传递我国的防疫政策信息,还可以更好地促进国际交流,帮助目标受众获得与源语于受众相同的文化感知。
Chapter One Introduction
1.1 Research Background
At the end of 2019,a number of cases of pneumonia of unknown cause weredetected in some hospitals in Wuhan,Hubei Province.In a short period of time,thenumber of infected people rose rapidly,and now experts have confirmed an acuterespiratory infectious disease caused by the COVID-19,which is a human infectiousdisease.Since then,as the epidemic has developed,confirmed cases have alsoappeared in other countries,and this attracted worldwide attention.According to theWorld Health Organization(WHO),the cumulative number of confirmed casesworldwide reached a high of 282 million in December 2021,including 5.41 milliondeaths.Due to the severity of the epidemic and the influence of international spread,pneumonia infected by the new coronavirus has become a public health emergency,and the World Health Organization officially named it COVID-19 on February 11,2022.
Because the first large-scale onset of the COVID-19 appeared/occurred in China,it attracted the attention and coverage of domestic and foreign media,which competedto report on how the Chinese government was controlling the COVID-19 and treatinginfected people.Controversies surrounding the COVID-19 often appear in news pagesor in the comments sections of websites,meanwhile,some foreign media have takenthe opportunity to slander China,calling it“the Chinese virus”.However,in fact,during the outbreak of COVID-19,the Chinese government and people have resistedthe COVID-19 bravely and tenaciously.The distorting news reports by foreign mediawere a kind of racism and a new challenge to China.Therefore,as one of the mostrepresentative and authoritative English language newspaper in China,it isparticularly important for China Daily to correct the false information reported insome news channel and tell the truth to the outside world.

1.2 Significance of the Research
1.2.1 Theoretical significance
Nida’s theory of translation has a significant influence on translation since the1980s.It is thought that Functional Equivalence Theory generated from Bible’stranslation,which provides tenable explanations that such a translation theory wasconcluded from a translation practice mainly about short sentences or extracts ofseveral clauses.Compared with other translation theory,Functional EquivalenceTheory is more suitable for analyses of short-clip speeches,such as the researchobject of the thesis—COVID-related words,usually found out from long paragraphs.Under the framework of Functional Equivalence Theory,it seems possible fordiscussion about the argument between particularity and universality,focusing ondomestic researches,about relevant texts of foreign publicity translated from Chineseto English.The thesis investigates the writing characteristics and translation strategiesof COVID-related texts.In addition,the concepts of national translation capacity,translation practice,foreign translation ability and related issues are also discussed,and the research theory on COVID-19-related texts translation is expanded.
Chapter Two Literature Review
2.1 Studies on Nida’s Functional Equivalence Theory
Eugene Nida,a famous American linguist,translator and translation theorist,isthe first person who put forward the idea of“formal equivalence”and“dynamicequivalence”in his book Towards a Science of Translating in 1964.He believed thatdifferent languages have obvious differences in form and meaning,therefore,formalequivalence was more theoretical while dynamic equivalence was more practical for itsought the most natural and maximum equivalence to the original information.Dynamic equivalence focuses on achieving natural expression in the target languagerather than keeping the form of the original text,while formal equivalence pays attention to the message itself,in both its form and content.This means that dynamicequivalence aims to create the same relationship between the target language text andits readers as the one between the source text and its readers.However,lexicalequivalence which was pervasive in translation circle for a long time,refers to findingwords in the target language that are not only equivalent in lexical meaning but also incultural connotation with the original language to make readers have the sameresponse as those in the original language.Such a rigid translation perspective maynot suit to a contemporary text of politics.Nida believed that functional equivalencecould be achieved through four aspects:the communication of language information,the transmission of spiritual style,the communication of language habits and thesimilar reaction of readers.The goal seems to be in accordance with analyses of thethesis which is to achieve equivalence in the most appropriate and natural language,which in turn means the target readers would have a similar reaction to the translationas the original readers had to the original text.
2.2 Studies on COVID-19-related Texts and their Translation
2.2.1Definition of the Text Related to COVID-19 and its Translation
Publicity translation is a type of translation that aims to introduce China to theworld in the context of globalization.It uses Chinese as the original language,Englishand other foreign languages as the means of expression,various media as theplatforms,and foreigners as the main audience.Publicity translation is aninternational communication across national boundaries,cultures and languages,itshould serve multi-functions in information dissemination,fact clarification andopinion competition for the sake of national image and interests Zhang Jian(2013).Translation of publicity texts refers to the translation of a large number of informationrelated to China’s economy,politics,culture and society from Chinese into English,the translation of COVID-19 related texts is an important part of it.
“The spread of COVID-19 is a global public health emergency,and the socialchanges caused by it will inevitably stimulate the emergence of new words.”(HouMin and Teng Yonglin,2020)In recent years,there have been many hot words andnew words with strong timeliness,such as方舱医院“temporary treatment centers;Fangcang shelter hospitals”,健康码“health code”.Abbreviations like“四早”措施(早发现、早报告、早隔离、早治疗)“the principle of early detection,reporting,quarantine and treatment”.Some words and expressions also appeared in the previous“SARS”epidemic prevention and control,but the public did not pay much attention tothem at that time.Due to the popularity of the Internet,these words have come intopeople’s view again in the fight against the COVID-19,they frequently appear inmedia reports and become hot topics,such as消杀(disinfection and sterilization)and留观(under medical observation),科学战疫(science-based approach in fighting theepidemic),绿色通道(green channel;fast transport channel),健康申报(declaration ofhealth status),疫情就是命令,防控就是责任(The epidemic calls us to action,and itis our duty to bring it under control;
Chapter Three Theoretical Framework .................... 17
3.1 Nida’s Functional Equivalence Theory ........................ 17
3.2 The Development and main notions of Functional Equivalence Theory ...................... 18
Chapter Four Application of Functional Equivalence Theory to the C-E Translation ofCOVID-19-related Texts ........................... 20
4.1 Functional Equivalence at the Lexical Level ................................... 20
4.1.1 Literal Translation ................................... 22
4.1.2 Literal Translation with Annotation ........................................... 26
Chapter Five Conclusion ......................... 54
5.1 Major Findings of the Study .......................... 55
5.2 Limitations of the Study ...................................... 56
5.3 Suggestions for Further Studies ................................. 56
Chapter Four Application of Functional Equivalence Theoryto the C-E Translation of COVID-19-related Texts
4.1 Functional Equivalence at the Lexical Level
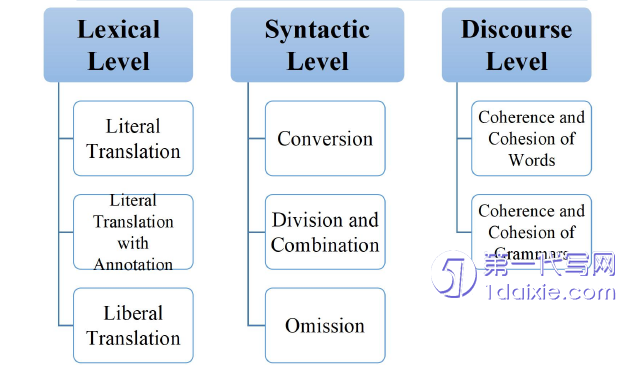
Functional Equivalence Theory emphasizes the reader’s response to thetranslated text,rather than the formal correspondence between the source and targetlanguages.Vocabulary is the basic unit of a language,and translation at the lexical level is the most basic part of translation activities.How to translate these words,abbreviations,phrases and expressions with Chinese characteristics and accuratelyintroduce China’s anti-epidemic policies and measures,is of great importance tobuilding China’s image in the world.Nida’s Functional Equivalence Theory caneffectively explain and guide the C-E translation of these words.“Translation shouldbe based on an accurate understanding of the original text,close to the reality ofChina’s development,close to the needs of foreign audiences for Chinese information,and close to the thinking habits of foreign audiences”(Huang,2004).Considering thereading habits of foreign readers,under the principle of lexical equivalence fromFunctional Equivalence Theory,literal translation,literal translation with annotation,liberal translation and so on.
Chapter Five Conclusion
5.1 Major Findings of the Study
The thesis conducts a thorough analysis,about COVID-related texts,of varioustranslation strategies,including literal translation,literal translation with annotation,liberal translation,conversion between active voice and passive voice,cohesion andcoherence etc.from lexical,syntactic and discoursal perspective within the frameworkof Functional Equivalence Theory.There is a concern that such kind of texts boasthuge potentials of publicity exchange with other countries.Therefore,the translatorshould take appropriate measures to keep the effective function of language whilestruggling to convey information.
Firstly,at the lexical level,grammatical structures and expressions should becarefully considered because of the differences between English and Chinese.Both ofliteral translation and liberal translation can achieve functional equivalence in theprocess of translating.Secondly,at the syntactic level,conversion of active sentencesto passive sentences,division,and combination and omission were studied.Specifically,in addition to the basic meaning of the sentence,the expression andreading habits of the target text should be fully considered to make the target textmore readable and acceptable for the target audience.Thirdly,at the discourse level,the equivalence can be achieved from the perspective of the coherence and cohesionof words and grammar.
reference(omitted)
