本文是一篇英语毕业论文,笔者认为对于科技类文本翻译而言,翻译重在达意,要概念准确、措辞严密,但不要求语言的艺术性,该类文本以实现传递信息之功能目的为主,译文不必达到与原文文字上的一一对应。鉴于文本中的专业术语较多,在翻译过程中,译者建立术语表。
Chapter One Task Description
1.1 Task Background
With human development entering 21st century,climate change has been gettingworse and worse,which intrigued countries around the world to pay more extensiveattention to this issue.Different types of causes give rise to climate change.One of them isthe natural factor,such as the change of solar radiation,variations in the Earth's orbitaround the Sun,volcanoes,atmospheric and oceanic circulation,and so on.Another is thehuman activity like greenhouse gas released by humans,reduction of forest and arable land,and booming population.The great ice age is one of the relatively unique times in thedevelopment history of the earth,so the research on the age will help humans to betterunderstand climate sensitivity and climate change.Addressing climate change is theresponsibility of all countries,and requires the joint efforts and cooperation of all mankind.The translation is an important bridge to communicate domestic and foreign cooperationand transfer domestic and foreign research achievements.Therefore,this translationpractice has practical significance.
The project is excerpted from The Great Ice Age:Climate Change and Life,which iswritten by Robin Wilson,S.Drury,and J.L.Chapman.In this book,the author introducesin detail climate-influenced factors and the interconnection of different parts of the earth'sclimate system.The translator chooses chapter two as the source material of this translationreport.There are six parts included in chapter two that the title is“Understanding Presentand Past Climate”:introduction,moving heat around,forcing functions and feedback,theevidence,understanding climate change,and summary.Chapter two mainly discusses thecontents of the definition and cause of climate,El Niño Events and La Nina phenomenon,thermohaline circulation,climate feedback system,and climate proxy data.
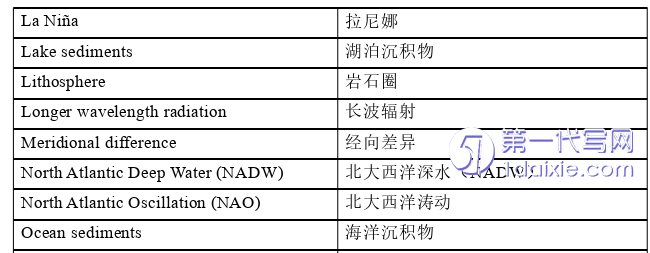
1.2 Significance of the Translation
As the translator mentioned above,climate change has given rise to attention aroundthe world.Coping with climate change requires the joint efforts of all mankind.Thistranslation can add a brick to the communicative bridge between home and abroad onclimate study.Moreover,a high-quality translation can not only help Chinese scholars toknow foreign research achievements on climate change,but also help the translatorimproving her translation ability,increasing knowledge,and enhancing the consciousnessof the Community of Shared Future for Mankind.
The source material belonged to geological text,is professional in expression,formalin language,and rich in vocabulary in geography and climate.With a lot of passive andlong sentences,it has characteristic language features and abundant scientific knowledge.Translating this text can provide researching and reading materials and referencetranslation to experts and scholars in the field of geological text translation,translators,andreaders interested in scientific translation.
Chapter Two Translation Process
2.1 Pre-translation
In order to make the translation task going smoothly,the translator does some worksto understand the original text deeply before translating,which are analyzing the sourcetext,selecting texts and translation tools.
2.1.1 Analysis of the Source Text
The Great Ice Age:Climate Change and Life,which is written by Robin Wilson,S.Drury,and J.L.Chapman,mainly studies climate change and life in the great ice age frompaleobiology,paleogeology,and paleoclimatology.The excerpt that the translator choosesas the source material is chapter two which mainly discusses climate-related content.Chapter two studies how forcing factors of the climate system may change the climate andhow feedback mechanisms may reinforce or limit the effects of such factors.
The source text is a typical scientific and technological text and has a large amount ofprofessional knowledge that involves geology,physics,astronomy,chemistry,computer,and other fields,so the passive mood,complex and long sentences,and professional termsare widely used in it.The aim of this text genre is to tell a fact by analyzing correspondingdata,as the author mentions in the introduction of chapter two that this book is written onthe assumption that its readers already have a sound understanding of the workings of theclimate system today,so the content and language usually are difficult for ordinary readersto understand.
2.2 While-translation
The translator divides this part into two stages.The first stage is to read the whole text.In the process of reading through the text,the translator marks the terms and difficultwords in the text and searches on the online dictionary to find the Chinese expressionscorresponding to these terms and words.Then,the unsolved words are put in the text,andthe search engine is used to check whether there are other Chinese expressions afteraccurately understanding these words in the context of the source text.Phase two is thetranslation of the full text.At this stage,many syntactic problems appear.English is farfrom Chinese.An English sentence can expand information by adding modifiers andclauses,while Chinese often uses a few short sentences to convey a message.Thus,inorder to make the translation readable and faithful to the original text,the translator needsto straighten out the logical relationship among the elements in a sentence in the originaltext according,and then translate it into Chinese that conforms to the Chinese style to theguidance of the Skopos Theory.
Chapter Three Theoretical Basis .............................. 7
3.1 A Brief Review of the Skopos Theory ............................... 7
3.2 Application of the Skopos Theory to the Translation of Sci-Tech Text ............................... 9
Chapter Four Case Analysis ............................ 12
4.1 Case Analysis at the Lexical Level .............................. 12
4.1.1 Translation of Verbs ..................................... 12
4.1.2 Translation of Professional Terms .................... 15
Chapter Five Conclusions .................................. 27
5.1 Limitations ................................. 28
5.2 Reflections .................................. 28
Chapter Four Case Analysis
4.1 Case Analysis at the Lexical Level
A word is the smallest unit of a sentence,and its translation affects the meaning of asentence.English verbs are often polysemous,and the use of verbs in sci-tech texts isdifferent from other texts.Therefore,in this translation practice,the translator needs toaccurately understand the meaning of the original text,and select the correct meaning ofthe verb in the context,so that the translation of the verb not only conforms to thecharacteristics of sci-tech texts but also accurately transmits information.Introducing andspreading information about science and technology,a sci-tech text inevitably has a widerange of terms.The translation of terms affects the information transmission and stylisticstyle of the target text.Therefore,in this section,the translator will analyze the text of thispractice from the translation of both verbs and terms under the guidance of the SkoposTheory.
4.1.1 Translation of Verbs
The verb is indispensable in English.The verb is the core of the sentence anddetermines the meaning of the whole sentence.Notional verbs have full lexical meaning oftheir own,and an English notional verb may correspond to several different Chinesemeanings.The meaning of a notional verb should be selected prudently in combining thecontext to avoid the target text being far away from the original text.In addition,thetranslator noticed in this translation practice that modal verbs are often used in the originaltext.Modal verbs can be used to express the attitude of the speaker,and also forspeculation.In the sci-tech text which pursues objectivity,modals can describe thingsobjectively and accurately better,so the translation of modal verbs also plays an importantrole in this translation practice.

Chapter Five Conclusions
5.1 Limitations
Under the guidance of the Skopos Theory,the translator solves some problems,butshe still has her own limitations.
Firstly,since the translator is not familiar with paleoclimate and geological scienceand lacks knowledge of them,she didn’t have a deep understanding of the professionalterms in the source text,which make her spend a lot of time supplementing theseknowledges so that leads to inaccuracy to some extent.Secondly,the translator does notunderstand the Skopos Theory enough,so she made a superficial analysis of the translationproblems encountered,without touching the deep inner of the Skopos Theory.
After summarizing her shortcomings,the translator believes that she should furtherstudy the connotation of the Skopos Theory,deepen the understanding of it,so can betteruse the Skopos Theory to guide the translation practice in the future translation,to solvetranslation problems.Secondly,the translator is well aware of how big a challenge it is totranslate unfamiliar texts.If the translator lacks the background knowledge of a text,he orshe must do his homework before translating to quickly learn the relevant backgroundknowledge,and when encountering professional difficulties in the translation process,heor she must consult the relevant books and references in time.Only in this way cantranslation errors be effectively avoided.Finally,translators must learn to use a variety oftools,including but not limited to dictionaries,online resources,official websites,etc.Aqualified translator must be a compound talent.Merely mastering Chinese-Englishtranslation does not make a qualified translator.Only by adhering to the realistic,pragmatic,serious and responsible attitude,constantly expanding the horizon of knowledge,specializing in honing the translation ability,can a translator become qualified.
reference(omitted)
