本文是一篇英语毕业论文,本实践针对语义和语用两个层面的多种隐性信息,译者在明晰化理论的指导下,分别提出相应的翻译方法。针对语义层面的隐性信息,译者采用替代和释义两种翻译方法,针对语用层面的隐性指称信息、隐性逻辑信息和隐性文化信息,分别采用具体化、结构重组和增译的方法。
1 Task Description
1.1 Background of the Task
Rome:An Empire’s Story was first published by Oxford University Press in 2012,and in 2022,the second edition was published,with more new research findings added inby the author.The translation task is based on the second edition.The author of the book,Greg Woolf,discusses the vicissitudes of Rome and the reason behind them based on thecutting-edge studies of scholars.Greg Woolf is a British ancient historian,archaeologistand academic,specializing in the late Iron Age and the Roman Empire.He has worked onformation of the provincial cultures,often using archaeological materials,and also on thecosmopolitan cultures of the metropolis.Much of his work considers the Roman worldfrom a global perspective.
Rome is an important entity in western history,even in world history.The empire,started from a city,strengthened itself gradually,and became a vast empire surroundingthe Mediterranean,which lasted over a thousand years and significantly influenced thesocial formation of Europe.Under the background of globalization nowadays,knowingthe history of other nations is of benefit to us,and the history of Rome,as a significant one,is worth knowing and popularizing,in this way,a book telling Rome’s history isworth translating.
1.2 Choice of the Text
The text is chosen both for its practical and academical significance.The practicalreason of choosing this book includes three factors:First,as is discussed before,thehistory of Rome is worth knowing and popularizing;Second,the author of the book is apremium expert in Rome history and has his unique perspective to introduce Rome;Third,the book,written by a historian with his expertise,is a good one for readers to knowabout Rome as well as its long-lasting impact,so as to understand important aspects ofwestern culture and society.The academical significance of the task lies in the greatamount of implicit information the text contains,which can be classified and translatedunder the guidance of explicitation theory,and thus can bring some help to the translationof historical text with much implicit information.
2 Process Description
2.1 Preparation before Translation
For the translation of the first two chapters of Rome:An Empire’s Story,threeparticipants were involved.One was the translator himself,who was responsible fortranslating the text,and two of his classmates were for proofreading.
Before translation,the translator searched the National Digital Library of Chinaand other websites at home and abroad,finding that there was no Chinese version ofRome:An Empire’s Story by the time when the book was chosen.Then,the translatorroughly read the whole book and thought that the book was within his means.Beforesetting out to translate,the translator searched the Internet to find out more about theauthor of the book and read the preface in depth to grasp the book’s content.To betterunderstand the historical background and related information in the text,as well as graspthe style of target text,the translator read some materials about Rome history both inEnglish and Chinese.
To finish the translation task in an orderly way and produce high-quality outputwithin time limitation,the translator made a schedule of finishing the translation,which covered the whole task process.
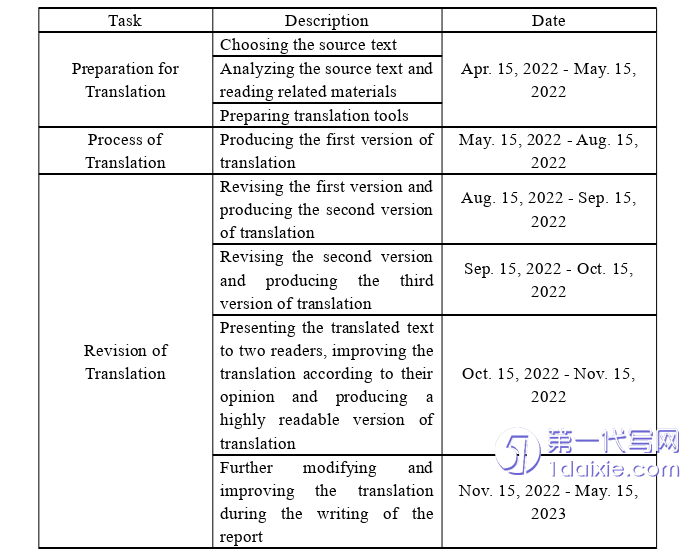
2.2 Process of Translation
Process of translation took the longest time in the whole translation task,duringwhich the translator should not only try to transcribe the words into Chinese,but also dealwith the cultural and history related expression.
In producing the first edition of translation,the translator used“Trados”tofacilitate translating.With the help of this tool,the whole text was divided into manysegments by sentences,each of which could be marked as“translated”or“untranslated”.Therefore,the translator could conveniently check the sentences to avoid ignoringcontents.Besides,with the help of terminology bank and translation memory in the tool,the translator could improve efficiency and ensure consistency.During translation process,the translator encountered many names,places,and professional knowledge that appearin the text,then the translator would search the internet and read related books andmaterials to make sure that the translation is suitable.This process is also a process inwhich the translator continually considered the unique aspects of the text and looked forsolutions to the challenges of translation.
With the help of CAT tools and the Internet,the translator translated about 200words every day.For this period,the translator marked some intractable contents to besolved in later processes in revision and also paid close attention to implicit informationin the text,marking some of examples for follow-up studies.
3 Case Analysis .................................. 8
3.1 Theoretical Framework ............................ 8
3.1.1 An Introduction to Explicitation Theory ...................................... 8
3.1.2 The Application of Explicitation Theory ................................... 10
4 Conclusion .......................................... 38
4.1 Major Findings ......................... 38
4.2 Limitations ...................................... 40
4.3 Suggestions ......................... 41
3 Case Analysis
3.1 Theoretical Framework
Translation is a process involving both understanding and expressing,during whichthe differences between two languages play important roles.Due to the culturaldifference and habitual language expression,some of the information of the original textmay not be understood directly by readers of the target text.In this process the translatormay make some of this information explicit consciously or unconsciously.This partintroduces the theory about this phenomenon,explicitation theory,which can guide thetranslation of implicit information.
3.1.1 An Introduction to Explicitation Theory
Explicitation was first put forward by Vinay and Darbelnet in 1958 as“the processof introducing information into the target language which is present only implicitly in the source language”.Later,Blum-Kulka(2000)formulated explicitation hypothesis,arguingthat the translation of the source language text would lead to more redundancy in targetlanguage text because of the differences of the two languages.According to Dai and Xiao(2010),a series of empirical studies on the hypothesis of explicitation,based on alarge-scale translation corpus of various languages,are conducted by researchersrepresented by Baker,Klaudy,Olohan,etc.,who research on explicitation of Englishtranslation,and Wang Kefei,He Xianbin,etc.,who focused on the explicitation ofChinese translation.Klaudy(1998)summarized the previous opinions and classifiedexplicitation into four categories—obligatory explicitation,optional explicitations,pragmatic explicitation and translation-inherent explicitation,the last category ofwhich,“translation-inherent explicitation”,is related to“explicitation hypothesis”.

4 Conclusion
4.1 Major Findings
During translation process,the translator finds that the source text contains muchinformation that is not explicitly expressed and may influence readers’understanding ofthe source text.This kind of information is implicit because of many reasons.
By consulting some linguistic materials and studies about implicit information,thetranslator separately analyzes implicit information at semantic level and pragmatic level.Implicit information at semantic level refers to the meaning encoded implicitly inlanguage itself,mainly in words or phrases.And implicit information at pragmatic levelrefers to the information concealed not in meaning but in context,which needs to beclarified through referring to different sentences or cultural knowledge.And at pragmaticlevel,implicit information in source text can be further divided according to the differentway in which the information is hidden in the text.For the translation of implicitinformation,the translator concludes with five practical methods to apply at differentlevels and in different kinds of text.
For implicit information at semantic level,substitution and paraphrase are used totranslate.Substitution is mainly used to deal with the implicit information caused by flexible use of words.Some of the words used in source text contain implicit informationbecause they are not expressing its original meaning and may cause misunderstanding toreaders,especially to readers of a different language.Substituting these words with morefrequently used words can facilitate understanding and realize the explicitation of theirimplicit information.The method of paraphrase is used when some of the words orphrases contain much implicit information that can not be simply expressed by usinglanguage units of the same forms as in source text.Paraphrase is used based on the fullunderstanding and analysis of source text,after which the translator uses more flexibleexpression to realize the explicitation of some information.
reference(omitted)
