本文是一篇英语毕业论文,本文研究结果证明,学生能够提供准确的同伴反馈,并根据反馈的准确性有选择性地采纳反馈评语。
Chapter One Introduction
1.1 Research Background
Among four basic skills of Engxish learning, writing ability is the most comprehensive one, requiring students to combine what they have learned in vocabulary, grammar and sentence. Producing a coherent, fluent, extended piece of writing is the most difficult thing in language learning (Nunan, 2001). Therefore, how to effectively teach writing and help students improve their writing ability is of great importance for both teachers and students.
In writing approach, recent years has seen the shift from the Product Approach to Process Writing Approach. Process Writing Approach puts emphasis on the importance of students’ participation in writing process, such as collection of information, formulation of writing plan and completion of writing. In writing assessment, recent years have witnessed the popularity of assessment for learning, which means using assessment to inform and improve learning. Different from learning for assessment of learning, which focuses on the final score, assessment for learning is beneficial for students to develop confidence, motivation and learning autonomy in writing. With the popularity of the new teaching method and assessment orientation, peer feedback has drawn many scholars’ attention.
1.2 Research Objectives
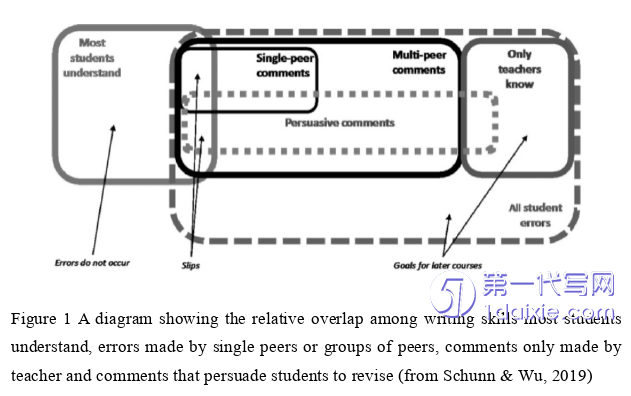
Peer feedback enables students to actively participate in the writing process because it demands communication, consultation and cooperation so that students can share their ideas (Zhou, 2013). While providing comments, students develop a sense of audience and know more about their strength and weakness. Peer feedback comments play an important role in improving their writing performance, skills and promoting critical thinking. Previous studies focusing on peer feedback revision looked into peer feedback accuracy and rarely directly focus on the casual relationship between peer feedback accuracy and implementation and subsequent revision. Therefore, the study intends to achieve three objectives through the analysis of participants’ writing and comments. Firstly, the peer feedback accuracy will be assessed based on the relevancy and correctness in addressing a draft problem. Secondly, we focus on the implementation of comments and predictability of peer feedback accuracy on implementation. Thirdly, to explore the predictability of peer feedback accuracy on revision improvement, the multiple linear regression was conducted. In addition, to know the influence of peer feedback accuracy on peer feedback revision, the revisions are classified based on the source, peer feedback accuracy and success among different revision types.
Chapter Two Literature Review
2.1 Peer Feedback Accuracy
In this section, the definition and measurement of peer feedback accuracy are illustrated and the studies on peer feedback accuracy are introduced.
2.1.1 Peer Feedback Accuracy and Its Measurement
Peer feedback accuracy has been defined as a binary term or defined based on multiple criteria in different research. Peer feedback accuracy is also one of the components of peer feedback quality in some research. The definition and measurement of peer feedback accuracy are introduced in the following part.
Peer feedback accuracy of revision-oriented comments has been examined in the previous studies (Caulk, 1994; Gielen et al., 2010; Hu, 2006; Hu & Lam, 2010; Mehrpour et al., 2023; Wu & Schunn, 2022; Yang et al., 2006; Jiang et al., 2022). In some research (Caulk, 1994; Chong, 2017; Hu, 2006; Hu & Lam, 2010; Yang et al., 2006; Jiang et al., 2022), peer feedback accuracy was coded in a binary way, accurate or inaccurate, valid or invalid. Caulk (1994) coded each students’ suggestion as valid or invalid Chong (2017) examined the influence of linguistic accuracy on the accuracy of written feedback they provide. Accuracy of students’ written feedback was perceived as writing with accurate grammar; students gave accurate written feedback when they could identify the errors related to the use of grammatical errors made by their peers correctly. Hu (2006) and Hu & Lam (2010) defined valid peer suggestions as revision-oriented comments that could lead to improvement on the writing when incorporated properly in revision. Mehrpour et al. (2023) defined the peer feedback accuracy based on whether the comments was accurate and whether comments aligned with the existing problems. Yang et al. (2006) followed the ”usable” feedback in Hyland’s (1998) terms: usable comments mean symbols and marks in the margins, underlining of problems, and complete corrections, as well as more detailed comments and suggestions. In Wu and Schunn (2022)’s study, problem identification accuracy referred to whether assessors correctly identified problems that actually exist.
2.2 Peer Feedback Implementation
This section presents relevant previous studies including studies on peer feedback implementation as well as studies on peer feedback accuracy and implementation.
2.2.1 Feedback Implementation in Peer Review
Peer feedback implementation refers to accepting peer’s suggestions and using them in subsequent draft. Implementation is a step to judge effectiveness of interaction between learners. Although implementation is not the same as learning, implementation at least reflects that feedback draws attention to a problem and triggers corresponding behaviors (Gao et al., 2019). The higher the proportion is, the more likely it is for peer review to be useful. However, a high proportion of suggestions alone is not enough. Suggestions not only need to be taken up by students in revision but also exert an impact on the quality of revised writing. Research in peer feedback implementation mainly focus on the feedback implementation rate, what kind of feedback students implemented and the effects of implemented comments on peer feedback revision.
The feedback implementation rate indicates how much peer feedback is actually incorporated into the final revision, one of the indicators of the helpfulness of feedback. Based on previous study (Connor & Asenavage, 1994; Hu & Lam, 2010; Mendonca & Johnson, 1994; Nelson & Carson, 1998; Nelson & Murphy, 1993; Paulus, 1999; Patchan & Schunn, 2016; Tsui & Ng, 2000; Min, 2006; Rollinson, 1998; Villamil & De Guerrero, 1998; Yang et al., 2006; Kong & Li, 2013), the peer feedback adoption rate is fluctuating to varying degrees in different contexts.
Chapter Three Methodology ......................... 23
3.1 Research Questions .......................... 23
3.2 Research Context and Participants .......................... 23
3.3 Peer Review Procedures ...................... 24
Chapter Four Results and Discussion .............................. 29
4.1 Peer Feedback Accuracy in Addressing Writing Problems ............................ 29
4.1.1 Major Problems in Students’ Writing ................................ 29
4.1.2 Peer Feedback Accuracy in Addressing Problems ...................... 32
Chapter Five Conclusion ............................ 55
5.1 Major Findings ........................................ 55
5.2 Implications of the Study .................................... 56
5.3 Limitations and Suggestions of the Study ............................... 57
Chapter Four Results and Discussion
4.1 Peer Feedback Accuracy in Addressing Writing Problems
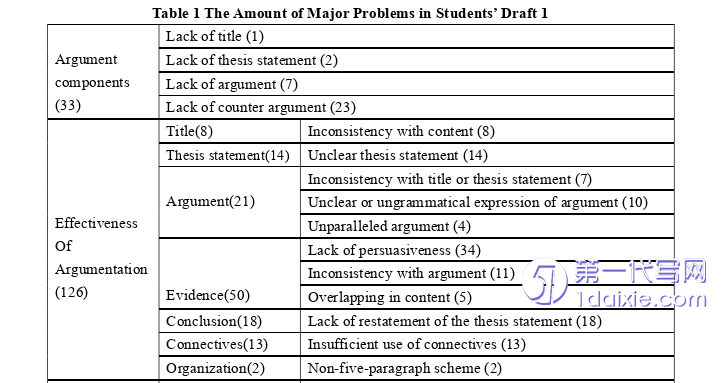
This section summarizes the major problems in students’ draft one in argument components, effectiveness of argumentation, grammar and vocabulary and language style. As mentioned in Chapter 3.5, there are 1773 comments identifying problems and providing suggestions or solutions. To answer the first question, the 1773 peer feedback are coded and the peer feedback accuracy in different dimensions and sub-dimensions is illustrated in this section.
4.1.1 Major Problems in Students’ Writing
4.1 Peer Feedback Accuracy in Addressing Writing Problems This section summarizes the major problems in students’ draft one in argument components, effectiveness of argumentation, grammar and vocabulary and language style. As mentioned in Chapter 3.5, there are 1773 comments identifying problems and providing suggestions or solutions. To answer the first question, the 1773 peer feedback are coded and the peer feedback accuracy in different dimensions and sub-dimensions is illustrated in this section. 4.1.1 Major Problems in Students’ Writing component is the lowest, 33 problems in this dimension. The number of problems in each dimension and sub-dimension is illustrated in Table 1.
Chapter Five Conclusion
5.1 Major Findings
Three major findings are summed up in response to three research questions based on a detailed analysis and discussion including the peer feedback accuracy, peer feedback implementation, the predictability of peer feedback accuracy on implementation as well as writing improvement and peer feedback accuracy and revision.
1) There are problems in students’ writing in terms of argumentative components, the effectiveness of argumentation, grammar and word choice as well as language styles. Based on the existing problems, students provide peer review comments. After coding, there are 1773 comments identifying problems and providing suggestions or solutions. The implementation rate of all comments is 73.32%. The implementation rate of identifications and suggestions is 74.16%. and 72.41% respectively. Consider the four dimensions in argumentative writing, the accuracy rate of comments in argument components, effectiveness of argumentation grammar and vocabulary and language style is 86.21%, 74.67%, 78.92% and 69.52% respectively.
2) In terms of implementation of comments, the implementation rate of comment is 35.70%. The accuracy rate of accurate comments is 46.08%, outnumbering that of inaccurate comments, 7.40%. Two-level logistic regression analysis revealed that peer feedback accuracy is a significant factor in predicting implementation of comments and that the implementation of accurate comments was 7.63 times more than that of inaccurate comments. With accuracy of comments identifying problems as the predictor, the two-level logistic regression analysis demonstrates that the implementation of accurate identifications is 6.62 times more than implementation of inaccurate identifications. With accuracy of comments providing suggestions as the predictor, the two-level logistic regression analysis demonstrates that the implementation of accurate suggestions is 9.01 times more than implementation of inaccurate suggestions. With accuracy as the characteristic of the two types of comments, suggestions or solutions are more likely to be implemented.
reference(omitted)
