本文是一篇英语毕业论文,本研究丰富了复杂理论的研究成果,细化了概要写作对英语专业学生写作能力的影响。基于二语写作的非线性发展特点和本研究的研究结果,教师可以根据不同类型的原型模型,将过程评价和形成评价相结合,对写作能力进行综合评价。
Chapter One Introduction
1.1 Research background
English writing skill has long been a popular topic of discussion in the field of second language acquisition. Many studies have emphasized the importance of measuring language competence and production quality through the dimensions of complexity and fluency, which are also the main research focuses in the field of second language acquisition.
A large number of studies have shown that English writing has a certain relationship with English reading. Students who read a lot, their writing competence is generally good. Summary writing can combine reading and writing. Summary writing is a comprehensive language activity combining reading and writing. Basing on the original text, students need to select and extract the main ideas and main points of the original text, and finally write a summary in their own language. Before writing a summary, students need to read the original text and distinguish the main ideas and main points, which show students’ reading competence. In writing, students need to paraphrase sentences with their own language, such as replacing synonyms, constructing the upper word, converting parts of speech, adjusting sentence structure, etc. This process shows students’ lexical knowledge and grammar knowledge. Students can also immediately apply the expression and cohesion methods learned from reading in summary writing. By continuing this activity for a semester, students’ English writing competence may be affected by this practice. Summary writing not only can use writing competences to complete complexity language tasks, but also can further promote the development of these language competences, which finally is conducive to improve students’ English competence.
1.2 Research significance
Due to the growing educational demand for English which is an international language, there is an urgent need to improve the writing competence. In order to achieve this goal, various kinds of teaching strategies have been proposed by experts, such as reading after writing, summary writing, and reading-to-writing pattern and so on. However, there are few diachronic studies on the effect of summary writing on writing competence, and few previous studies on fluency study textual cohesion. Therefore, English writing competence is shown through the development of summary writing. And this study will discuss writing competence from the perspective of complexity theory, explore the prototypes, compare the development trend of macro and micro writing competence, and then seek to put forward some targeted suggestions to help learners improve their writing competence. This study aims to explore the impact of summary on English majors’ writing competence, which has the following two aspects of theoretical and practical significance.
On the theoretical level, based on previous studies, this study will discuss the influence of summary writing on students’ English writing competence, which not only echoes a large number of previous research results, but also makes up for the shortcomings of previous studies. It enriches the research results of complexity theories and refines the influence of English summary writing on students’ writing competence.
Chapter Two Literature Review
2.1 Summary writing
This section first introduces the definition of summary writing by different scholars. The second part is the research on summary writing. The final part is application of summary writing.
2.1.1 Definition of summary writing
Summary Writing is explained in the Collins Advanced Dictionary as: “A summary of something is a short account of it, which gives the main points but not the details.” Wikipedia gives the definition as “shortening a passage or a write-up without changing its meaning but by using different words and sentences.” With the development of second language research, the definition of summary writing is becoming more and more perfect and comprehensive.
Early summary writing is more constrained than normal foreign language writing. Kintsch and Van Dijk (1978) believed that the author should first understand the text, and then find out and organize the main points of the article. In the end, the author restates the content in his own words, in which the author’s initiative is not reflected. Irwin (Irwin, 1986:5) simply defined summary writing as the synthesis and summary of text ideas. Ding et al. (1994) only regards summary writing as a simple reiteration of the basic ideas of the original text. Miya (2001) believes that summary should shorten the length and complexity of the text, but retain as much information as possible in the original content. Ding and Wu (1997) argued in their English Manual Writing that “summary writing is to extract the main points of articles and write them independently”.
2.2 English writing competence
2.2.1 Measurement of English writing competence
Writing competence is a comprehensive language competence, and different scholars have different standards to measure writing competence. So far, scholars have not reached a consensus on the composition and measurement criteria of second language writing competence. Yuan and Ellis believe that writing is a logical and systematic process of elaborating ideas through the flexible use of grammar (Yuan & Ellis, 2004). Canale and Swain (1980) put forward the concept of communicative competence, arguing that writing competence is a kind of communicative competence. Communicative competence includes grammatical competence, linguistic competence, structural competence and strategic competence. Bereiter and Scardamalia (1987) pointed out that writing competence consists of five main elements. Cumming (1989) believes that second language competence and writing competence together constitute second language writing competence. The competence of second language learners to freely use second language vocabulary and syntax is second language competence. The second language writing competence only includes the learner’s genre awareness and the writing reader. Although there is no unified standard, scholars agree that human language is a complexity behavior, so the structure of the product measured by second language learners should be multi-dimensional. Skehan (1998) proposed complexity, accuracy and fluency. CAF can reflect the multi-dimension of second language performance. Yuan and Ellis (2004) also suggested evaluating writing competence in terms of accuracy, fluency, and complexity. At the same time, since the study of Wolfe-Quintero, Inagaki and Kim was published in 1998, CAF as a measure has been widely used in second language acquisition studies. Therefore, according to the research content, this study evaluates writing competence from two aspects: fluency and complexity.
Chapter Three Theoretical Basis ........................ 18
3.1 Introduction of complexity theory ............................... 18
3.2 Three schools of complexity theory ................................ 20
Chapter Four Research Methodology ...................................... 24
4.1 Research questions ............................. 24
4.2 Research corpus .............................. 24
Chapter Five Results and Discussion ........................... 32
5.1 Development of students’ complexity in summary writing ............................ 32
5.1.1 Students’ lexical complexity in summary writing ................................ 32
5.1.2 Students’ syntactic complexity in summary writing ............................. 37
Chapter Five Results and Discussion
5.1 Development of students’ complexity in summary writing
Complexity includes lexical complexity and syntactic complexity. In order to answer the first question and have a deeper understanding of the development of samples, this study explores the changes of L2 writing features from the two dimensions of lexical complexity and syntactic complexity.
5.1.1 Students’ lexical complexity in summary writing
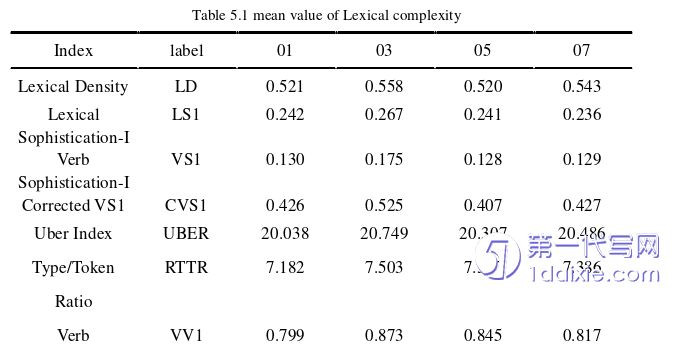
Preview summary is imported into The Lexical Complexity Analyzer (LCA) for calculation, which Calculates the change of each index. In this study, four times of data were selected at the same interval, and the mean values of these 12 indicators were extracted. The purpose is to explore the fluctuation characteristics of students’ lexical complexity and the changes of students’ vocabulary in micro indexes. The results are shown in Table 5.1.
Chapter Six Conclusion
6.1 Major findings
This study analyzed preview summary texts of 93 English majors. The purpose is to understand the overall development of students’ complexity and fluency in summary writing, and prototypes of complexity and fluency. All of this also explores development of English majors’ L2 summary writing competence from the macro and micro level, during their first semester. The study made the following findings.
First, the overall complexity of summary writing is in a positive trend. In terms of lexical complexity, the density of content words and lexical diversity of students increased significantly. In terms of syntactic complexity, the average sentence length of students increased significantly. The ratio of compound phrases to clauses and the ratio of complexity noun phrases to clauses increased significantly. In all this summaries, the increase of verb diversity and adverb diversity was not significant, and mean of lexical complexity, verb complexity, and modified verb complexity did not increase. This is consistent with previous studies, that is, the writing level is not in direct proportion to the rate of using low-frequency words. The increases in the mean length of clauses, the mean length of t-units, and the ratio of clauses to clauses are not significant. The reason has to do with the fact that the text type is summary writing.
Second, the overall trend of students’ written fluency is positive. Students’ competence of using conjunction was improved. Specifically, the reason is not only the improvement of language competence but also the increase of understanding of Chinese and Western thinking patterns. However, the insignificant increase of positive connectives is mostly related to Chinese students’ expression habits, and lacking of pragmatic awareness and logical awareness.
reference(omitted)
