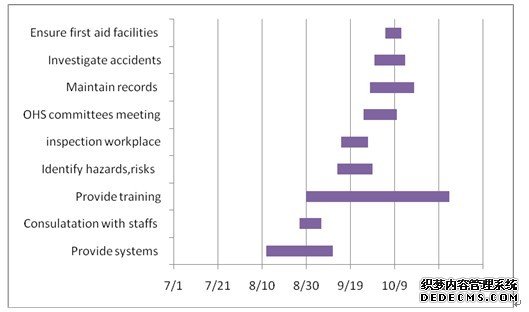
1. Create an Operational Plan for implementing the new OHS Management System:
|
ACTION REQUIRED
|
|||||
|
Action
|
what needs to be done
|
By Whom(who is responsible)
|
By Where(where it should be done)
|
By when
|
|
|
Follow the OH&S Management System policies and procedure
|
1.Provide and explain the OHSMS Guidelines and templates to staff. Include the Program as a standing item on workgroup and management meeting agendas.
2. Ensuring that establishment has in place effective policies, procedures and systems (including risk management systems) to ensure the health, safety and wellbeing of staffs and other persons who may be affected by its undertakings
3. Communicate OHS responsibilities to all staff at induction including casual staff, temporary staff, contractors and visitors
|
OHS Managers
|
In workplace
|
7.13
|
|
|
Training - developing skills and competencies
|
1. Identify and provide relevant OHS training and record the details. Induct new staff and students to familiarize them with OHS responsibilities and local procedures for managing risks.
2. Discuss OHS responsibilities at management meetings, staff meetings, team meetings, school development days and other relevant forums
3. Document staff OHS responsibilities
4. Identify OHS needs of staff and co-ordinate information, instruction and training to meet any deficiencies in staff competency in carrying out their duties
5. Information, instruction and training is reviewed periodically and revised when changes in processes occur
|
OHS Managers
|
In training center
|
7.15
|
|
|
Hazardous substances(including specific hazardous)
|
1.Label all hazardous substance containers correctly. Dispose of hazardous waste according to OHS guidelines
2. Identify hazards and assess risks through risk management process and visual inspections
3. Communicate responsibilities for reporting and repairs of electrical faults
4. Ensure hazardous electrical items are rendered inoperable and removed
5. Develop effective management strategies to identify, assess and control potential psychological hazards
6. Ensure staff have requisite skills and abilities to undertake their work
7. Provide information, instruction and training to staff to ensure correct procedures are followed.
8. Conduct workplace inspections to identify noise sources and implement noise control measures
9. Establish good housekeeping protocols and ensure floors, ramps, stairs, workrooms and storage areas are clean, dry and free of damage
10. Establish and maintain a system for chemical waste
|
Supervisors
|
In working area
|
8.1
|
|
|
Personal protective equipment
|
1.Assess the OHS implications of equipment and materials being purchased.
2. Follow departmental guidelines in relation to personal protective equipment
3. Ensure PPE conforms to the relevant Australian Standard
4. Relevant information, instruction and training is provided for all staff
5. Risk assessments on high risk manual handling tasks are conducted, safe working procedures developed, documented and implemented
|
All staff members
|
In Working area
|
8.16
|
|
|
Injuries and incidents are reported and investigated
|
1. Incident reports must be submitted on time i.e. within 24 hours. Supervisors investigate incidents in consultation with workgroup members and implement suitable risk control measures to prevent recurrence.
2. Maintain records of all hazard, incident and injury reports
3. Encourage staff to report accidents/incidents
4. Investigate accidents and take corrective action
5. Review accident/incident reports to identify trends
|
OHS Managers
|
In workplace
|
8.20
|
|
|
First Aid
|
1.Allocate responsibility for providing first aid and maintaining kits in accordance with guidelines, or identify and communicate the details of the First Aid Officer(s).
2. Ensure adequate first aid facilities and equipment are provided based on a risk management approach
3. Check first aid kits regularly and replenish as necessary
4. Review first aid facilities and determine where extra kits are needed
5. Display names and contact details of first aid officers in prominent locations
|
Supervisors
|
In workplace
|
8.26
|
|
|
Consultation
|
1. Provide staff with opportunities to regularly discuss OHS issues, eg. staff meetings, faculty/stage meetings and curriculum committee meetings
2. Develop a consultation statement and communicate to all staff
3. If an OHS Committee is in place, minutes are circulated and displayed on notice boards
4. Maintain consultation records
5. Schedule regular meetings for OHS committees, reps or other agreed arrangements
|
OHS Representatives
|
Meeting room
|
7.29
|
|
- Determining which safety programs are to receive priority
- Monitoring the outcome of an organisation’s health and safety programs
- Ensuring compliance with legislation and standards
- Endorsing the formulation of appropriate rules, procedures and methods for the workplace
- Ongoing and effective dissemination of OHS information and promotion of health and safety awareness in the workplace
- Overall supervision of employees to ensure the health and safety of the worker, the public and the consumer
- Hazard identification of particular safety programs
- On-the-job training and instruction
- Efforts to motivate employees to comply with safe work practices, including specific directives when giving orders
- Accident/incident investigation, correct reporting and notification according to legal requirements
- Issue of , and ensuring correct use and maintenance of , appropriate personal protective equipments
- Decision-making regarding job design, workplace layout and recruitment, where they have this authority.
- Conducts inspections personally or in company with executives and supervising officers, specialist consultants, or health and safety representatives/committee members to ensure the observance of health and safety standards and for the purpose of discovering unsafe or unsatisfactory conditions and practices before personal injury occurs. The health and safety officer/manager should be able to identify and qualify/quantify risks of injury or disease from occupational hazards and determine possible control measures.
- Reports any unsafe and unsatisfactory conditions, procedures or operations to the supervisor or executive in charge.
- Acts as adviser to executive and supervisory staff and employees in all matters concerning prevention of accidents, injury, hazard, disease and the promotion of health and safety. Monitors the organisation’s overall safety performance in order to report this to senior management.
- Maintains an injury record system generally in accordance with legislation and relevant standards.
- Attends all meetings of health and safety committees, and staff meetings or conferences when health and safety matters are discussed or considered.
- Ensures incident notification requirements are complied with.
- Organises health and safety training of staff and employees in conjunction with executives and supervisors. Institutes health and safety promotion campaigns to create and maintain an interest in health and safety at all levels. Conducts or arranges health and safety induction courses for new employees.
- Monitors and advises – on changes to legislation and award provisions relevant to health and safety, as well as the OHS implications of changes from all sources.
- Reviews, monitors and updates health and safety manuals, rules, procedures, etc.
- Dispense and control items from first aid cabinet
- Ensure cabinet supplies are adequate
- Treat minor wounds and injuries, such as applying dressings, stopping bleeding and treating burns.
- Record accident/injury details in accident book
- Arrange further assistance if required
|
|
Effective consultation
|
Ineffective consultation
|
|
When consultation occurs
|
Early, before agenda is set and decisions are made
|
After the agenda is set and decisions are made
|
|
Employer role
|
Interested in and values employees’ ideas
|
No recognition of the benefits of consultation
|
|
Employer skills needed
|
Interpersonal, facilitative listening
|
, No skills needed
|
|
Employee role
|
Pro-active, employees
encouraged to suggest
|
Reactive, employees have
no role in improving OHS ideas
|
|
Employee skills
|
Training provided in communication skills and risk assessment
|
No training provided to
enable effective participation
|
|
Process
|
Open and receptive to
employee participation
|
Invisible, barriers to employee participation
|
|
Information
|
Relevant information provided
|
Limited access to
information
|
|
Communication
|
Opportunities for one-to- one communication with employees, clear and
on-going feedback
|
No direct communication with employees, no feedback
|
|
Outcomes
|
Outcomes result in improvements to the systems for managing
safety
|
There is no improvement in how safety is managed
|
- Induction training
- Preparing training
- Different training needs for different levels
- Employees
- Health and safety representatives/committee members
- Supervisors
- Senior managers
- Information
|
Insured costs
|
Uninsured costs
|
|
Injuries
· Compensation for lost earnings
· Medical and hospital costs
· Awards for permanent disability
· Rehabilitation costs
· Funeral charges
· Pensions for dependants
· Public liability
Property damage
· Fire
· Loss and damage
|
Injures
· First aid expenses
· Transportation costs
· Cost of investigation
· Cost of processing reports
Wage losses
· Person hours spent in cleaning up the accident area
· Time spent repairing damaged
equipment
· Time lost by workers receiving first aid
Production losses
· Loss of skill and experience
· Lowered production of worker replacement
Associated costs
· Recruitment of workers for replacement of injured employee
· Training of replacement employee
Off-the-job accidents
· Cost of medical services
· Time spent on injured worker’s welfare
|
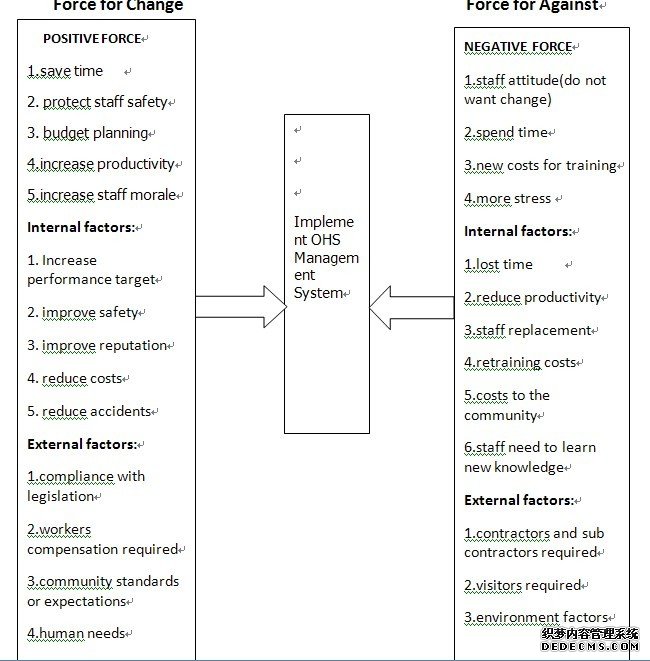
Force for Change Force for Against
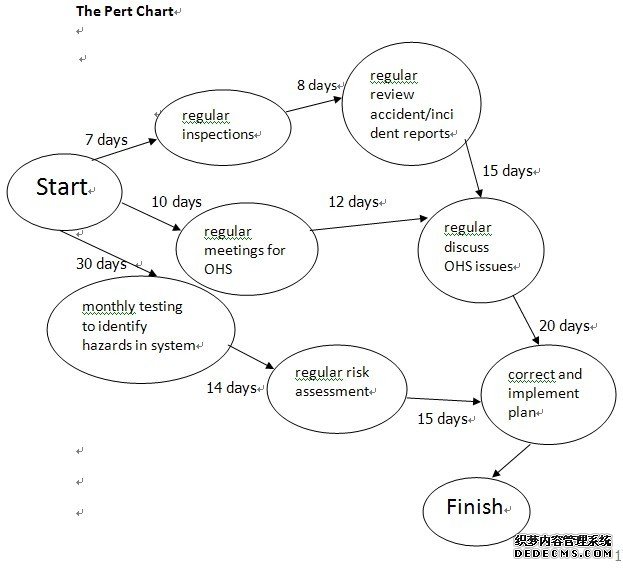
- The pert chart for identify and explain the success of your new OHS Management System.
|
regular review accident/incident reports
|
|
regular inspections
|
|
Start
|
|
monthly testing to identify hazards in system
|
|
regular discuss OHS issues
|
|
regular meetings for OHS committees
|
|
correct and implement plan
|
|
regular risk assessment
|
|
Finish
|
|
Item
|
What to look for
|
Conforms
Yes/no
|
Comments
|
|
Management responsibility and staffing
|
Is an effective contractor management system in place, and does it ensure proper risk management in relation to work done by contractors?
|
|
|
|
Accountability for health and safety
|
Is the OHSMS regularly reviewed by senior management to check its adequacy and effectiveness?
|
|
|
|
Inspecting the workplace
|
Are risk assessment and control records kept and, if so , have they been appropriately followed up and monitored?
|
|
|
|
Training and competence
|
Are checks made to ensure employees’ competence to carry out their task safely?
|
|
|
|
Cultivating safe attitudes, behaviour and practice
|
Does the organisation provide positive recognition for good practice?
|
|
|
|
Risk management
|
Does the organisation established and maintained documented procedures to identify hazards and ensure OHS risks are controlled?
|
|
|
|
Safety and health research
|
Is useful information being obtained from employers’ associations, insurance companies, OHS authorities, government departments or other sources?
|
|
|
|
Emergency planning and fire safety
|
Does the organisation have an emergency control plan in place?
|
|
|
|
Health and safety information, accident records and analysis
|
Are risk assessment and control records kept?
Is a register of injuries kept in an appropriate form?
|
|
|
|
The information provided in this questionnaire is an accurate summary of the
company’s occupational health and safety management system.
Company Name:_______________________________________________
Position:____________________ Name:____________________
Signed:_____________________ Date:_____________________
Contract Number:_____________
|
||||
|
Questions
|
YES
|
NO
|
||
|
OHS Policy and Management
|
1. Is there a written company health and safety policy?
|
|
|
|
|
2. Are health and safety responsibilities clearly identified for all levels of staff?
|
|
|
||
|
3. Does the company have an OHS Management System certified by a recognised independent authority?
|
|
|
||
|
Safe Work Practices and Procedures
|
1.Has the company prepared safe operating procedures or specific safety instructions relevant to its operations?
|
|
|
|
|
2. Are there procedures for storing and handling hazardous substances?
|
|
|
||
|
3. Are there procedures for identifying, assessing and controlling risks associated with manual handling?
|
|
|
||
|
4. Is there a documented incident investigation procedure?
|
|
|
||
|
OHS Training
|
1. Is health and safety training conducted in your company?
|
|
|
|
|
2. Is a record maintained of all training and induction programs undertaken for employees in your company?
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|||
|
Health and Safety Workplace Inspection
|
1.Are regular health and safety inspections at worksites undertaken and documented?
|
|
|
|
|
2. Are standard workplace inspection checklists used to conduct health and safety inspections?
|
|
|
||
|
3. Is there a procedure by which employees can report hazards at workplaces?
|
|
|
||
|
Health and Safety Consultation
|
1.Is there a workplace health and safety committee?
|
|
|
|
|
2. Are employees involved in decision making over OHS matters?
|
|
|
||
|
3. Are there employee elected health and safety representatives?
|
|
|
||
|
4. Is there a suitably qualified person(s) engaged to provide advice in relation to the OHS of employees?
|
|
|
||
|
OHS Performance Monitoring
|
1. Is there a system for recording analysing and improving
health and safety performance?
|
|
|
|
|
2. Are employees regularly provided with information on company health and safety performance?
|
|
|
||
|
3. Has the company ever been convicted of an
occupational health and safety offence?
|
|
|
||
- Describe in detail how you would report the progress back to the CEO.
- Development of a OHS Operational plans is one key way that senior managers provide leadership and commitment. This plan:
- report to CEO
