Banking Essay写作格式-电子现金的演变,本文是一篇留学生Banking专业的Essay写作格式参考范文,主要是解释电子现金是指在表示真实货币虚拟格式的技术设备上的货币价值电子存储。传统纸面货币体系的这种变革被认为是技术快速发展的里程碑式成果之一。电子现金所体现的某些强大力量,例如增强隐私和安全性,降低交易和处理成本,使得电子现金能够在一段时间内接管纸币。尽管电子现金带来的好处,但它也会对某些经济因素,如税收和洗钱产生不利影响。此外,电子现金对经济的渗透性低被认为是未来电子现金将面临的最大挑战之一。以下是Banking Essay写作格式的全部内容,是一篇符合国外大学Essay写作格式要求的范文,供参考。
Abstract 摘要
Electronic cash is referred to the electronic store of monetary value on a technical device representing a virtual format of real money. This transformation of traditional paper based monetary system is considered to be one of the milestone achievements of rapid technological developments. Certain powerful forces embodied with electronic cash such as enhanced privacy and security, reduced transaction and handling costs has allowed electronic cash to take over paper money over the time. Despite of the benefits associated with electronic cash it will also have adverse impacts on certain economical factors such as taxation and money laundering. Furthermore the low penetration of electronic cash into the economy is identified to be one of the biggest challenges electronic cash will face ahead into the future.
1. Introduction 简介
The World is moving rapidly with vastly changing technological developments and innovations. We are currently experiencing an era, where everything is getting automated and digitalized. Along with this technological transition, international monetary system is one significant aspect that is getting transferred from its current state of paper based monetary system to electronic monetary/cash system. According to the 1994 report of European Central bank, electronic cash can be defined as an "electronic store of monetary value on a technical device that may be widely used for making payments to undertakings other than the issuer without necessarily involving bank accounts in the transaction, but acting as a prepaid bearer instrument"[1]. Like the serial number on general dollar bills, electronic cash issued by a bank or any other institution will also consist a unique number and will represent a specified value of real money. Hence with the current accelerated phase of changes and innovation, money is becoming "virtual". In the sense, it is expressed as an "assemblage of ones and zeros which can be displayed on millions of computer screens throughout the world, can be transferred at the speed of light and yet is located nowhere" [2]. This research report will provide an analysis about Electronic cash in the following ways. The section 2 will present an overview of the rise of the electronic cash over the traditional paper money. The section 3 will elaborate the step by step process involved with electronic cash system.
随着技术发展和创新的巨大变化,世界正在迅速发展。我们目前正经历一个时代,所有的东西都在自动化和数字化。随着技术的转型,国际货币体系正从纸面货币体系的现状向电子货币/现金系统转移。根据欧洲央行1994年的报告,电子现金可定义为“在技术装置上的电子货币价值存储,该技术装置可广泛用于向发行人以外的企业支付款项,而不必涉及交易中的银行账户,但作为预付的无记名票据”。与普通美元票据上的序列号一样,银行或任何其他机构发行的电子现金也将包含唯一的数字,并将代表实际货币的特定值。因此,随着当前变革和创新的加速阶段,货币正变得“虚拟”。从这个意义上说,它被表达为“一个零和一个集合,可以在全世界数百万的计算机屏幕上显示,可以以光速传输,但却不在任何地方"。本研究报告将以以下方式对电子现金进行分析。第二节将概述电子现金相对于传统纸币的兴起。第三节将详细阐述电子现金系统所涉及的一步一步的过程。
The section 4 will describe different types of electronic cash while section 5 will provide examples of real world implementation of electronic cash. Furthermore the section 6 will emphasis on risks and issues associated with electronic cash while section 7 describes the challenges ahead for electronic cash.
第4节将介绍不同类型的电子现金,第5节将提供电子现金在现实世界中实施的实例。此外,第6节将着重讨论与电子现金有关的风险和问题,第7节则说明电子现金今后面临的挑战。
2. The rise of electronic cash 电子现金的兴起
In an economy without a standard medium of exchange, trades were executed based on different methods. Where as in the earliest period of human civilization people exchanged several commodities they possess in order to buy goods they required. This was referred as 'commodity money'. Later on commodity money changed into 'metallic money' where people traded based on certain metals such as gold, silver and copper. Thereafter with the progress in human civilization, the 'paper money' was invented marking a milestone in development of the monetary system. Even as at today paper money is extensively used for transactions within the economy. Nevertheless, the financial services been the early adopters of information technology, the concept of electronic cash, which is also known as virtual money was invented and introduced. As per the economic theories if anything to be considered as real money, it need to fulfill three important functions. They are, it should act as a medium of exchange, should have a unit of account and should have the ability to store of value [3]. Therefore it was guaranteed that electronic cash can be used as general medium of exchange as it fulfills all three criterias.
在没有标准交换媒介的经济中,交易是基于不同的方法进行的。人类文明最早时期,人们为了购买所需商品交换了自己拥有的几种商品。这被称为“商品货币”。后来,商品货币变成了“金属货币”,人们以黄金、白银和铜等某些金属为基础进行交易。此后,随着人类文明的进步,“纸币”的发明标志着货币体系发展的里程碑。即使在今天,纸币也被广泛用于经济中的交易。然而,金融服务业是信息技术的早期应用者,电子现金的概念也被发明和引入,也就是所谓的虚拟货币。根据经济学理论,如果有什么东西要被视为实物货币,就需要履行三个重要的功能。它们应该作为交换媒介,应该有一个账户单位,并且应该有储存价值的能力。因此,电子现金能够作为通用的交换媒介,因为它能满足这三个标准。
Gradually electronic cash got widely spread throughout the world as it embodied powerful forces that contributed to its success compared to existing forms of money. In comparison with paper money, which uses only physical security features, electronic cash use cryptography to authenticate transactions and to protect the confidentiality and the integrity of data [1]. Whereas both security and privacy of a transaction is determined by electronic cash. It must also be noted that banks currently incur large cost to handle notes and coins. For instance, in USA alone, the clearing of cheques cost financial institutions $60 billion per year [2].The handling cost of cash is that much high. Hence in the virtual world these handling and transaction costs are aimed to reduce. Electronic cash is considered as a superb accounting unit, as it can be converted from one currency to another, or be transformed into bonds or stocks almost instantly. It takes up virtually no room, it can be counted automatically, and it never wears out, rusts or tarnishes [2]. Furthermore electronic cash is superior to paper money for distant transactions [2]. While notes and coins need to be carried in bullet-proof vans manned by armed guards, electronic cash can be moved easily and quickly. Hence these properties have allowed electronic cash to take over paper money and mark a dominating position within the monetary system.
随着电子现金与现有货币形式相比,电子现金在世界各地的传播日益广泛,因为它体现了强大的力量,为其成功作出了贡献。与仅使用物理安全功能的纸币相比,电子现金使用密码技术对交易进行身份验证,并保护数据的机密性和完整性。而交易的安全性和隐私性都由电子现金决定。还必须指出,银行目前处理纸币和硬币的成本很大。比如,仅在美国,支票结算每年就要花费600亿美元,现金的处理成本就高得多。因此,在虚拟世界中,这些处理和交易成本的目的是降低。电子现金被认为是一个极好的会计单位,因为它可以从一种货币转换成另一种货币,或者几乎立即转化为债券或股票。它几乎不占用任何空间,它可以自动计数,而且它从不磨损,生锈或污损。此外,电子现金在远距离交易中优于纸币。虽然纸币和硬币需要装在武装警卫的防弹货车上,但电子现金可以轻松快速地移动。因此,这些特性使得电子现金可以接管纸币,并标志着在货币体系中占据主导地位。
3. The process involved with electronic cash 电子现金的处理
The basic idea of Electronic cash implementation involves at least three parties. They are, issuer not necessarily financial institutions, consumers as the end users who use the electronic cash and merchant who accept electronic cash in exchange with products or services provided [4].The steps involved with the process are as follows.
电子现金实施的基本构想至少涉及三个缔约方。发行人不一定是金融机构、消费者作为使用电子现金的最终用户和接受电子现金以换取所提供的产品或服务的商户。流程涉及的步骤如下。
Consumer needs to open an account with the bank. The merchant who need to participate in the electronic cash transactions will have to open multiple accounts with various banks in order to support customers who use different banks.
消费者需要在银行开立帐户。需要参与电子现金交易的商户,必须与各银行开立多个账户,以支持使用不同银行的客户。
When the consumer decides to purchase goods he or she will transfer the electronic cash from their account to his or her electronic purse. The electronic cash can then be transferred to the merchant. These transactions done through internet are normally encrypted.
当消费者决定购买商品时,他或她将电子现金从他们的帐户转移到他的电子钱包。然后电子现金可以转移到商家。通过互联网进行的这些交易通常是加密的。
Once the merchant received the electronic cash payment, he will then get it verified by the bank. The bank will then authenticate the electronic cash transaction. Upon verification merchant will deliver the goods to the consumer. At the same time bank will debit the agreed amount from the consumers account and deposit the same into the merchant's account.
一旦商户收到电子现金支付,他将得到银行的核实。银行随后将对电子现金交易进行认证。经核实,商户将将货物交付给消费者。同时银行将从消费者账户中借记约定金额,并存入商户账户。
4. Types of Electronic cash 电子现金类型
Following the above process of electronic cash implementation, electronic cash can be classified in two ways. In one way, electronic cash is classified based on whether it can be tracked or not. Under this category, electronic cash is divided as "identified electronic cash" and "anonymous electronic cash" [5].
按照上述电子现金实施过程,电子现金可以分为两种方式。在某种程度上,电子现金是根据是否可以跟踪来分类的。在这一类别下,电子现金分为“已识别电子现金”和“匿名电子现金”。
4.1 Identified Electronic cash 已识别电子现金
Identified electronic cash works more similar to a credit card. From the very first time it is issued by a bank to one of its customer, up to its final return to the bank can be easily tracked by the bank [5]. Consequently it allows the bank to track the payment throughout the economy, hence the bank will hold each and every detail of who the original customer is, and how he has spent the money. To make electronic cash identifiable like this, electronic cash contains a unique serial number that is generated by the bank itself. So that if the customer tried to spend the same money more than once, it can be easily caught and prevented. As per the graphical representation shown in Figure 1, the steps involved with identified electronic cash can be listed as follows.
电子现金的工作原理更类似于信用卡。从第一次由银行向其客户发行,直到最终返还给银行,银行都可以轻松跟踪。因此,它允许银行跟踪整个经济体的付款情况,因此银行将掌握原始客户是谁以及他是如何花钱的每一个细节。为了使电子现金能够像这样被识别,电子现金包含一个由银行自己生成的唯一序列号。因此,如果客户多次尝试花相同的钱,就很容易被抓住并防止。根据图1所示的图形表示,与已识别的电子现金相关的步骤可以如下所示。
The bank generates a serial number SR100, for electronic cash worth $100.
银行生成一个序列号SR100,用于价值100美元的电子现金。
The customer will purchase goods from a merchant, by spending electronic cash worth $100 and send the corresponding electronic file to the merchant.
客户将通过花费价值100美元的电子现金从商户处购买商品,并将相应的电子文件发送给商户。
The merchant will then go back to the bank handover the electronic cash and get real money in exchange.
然后,商户将返回银行,交出电子现金,并获得真正的货币作为交换。
At this point the bank receives the electronic cash with the serial number SR100 back. Therefore the bank knows that the customer has spent the electronic cash on a specific date to buy a specific product from a specific merchant.
此时,银行收到序列号为SR100的电子现金。因此,银行知道客户在特定日期使用电子现金从特定商户购买特定产品。
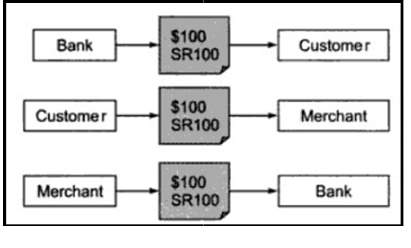
Figure 1: Steps involved in identified electronic cash [5]. 涉及已识别电子现金的步骤
4.2 Anonymous electronic cash 匿名电子现金
Anonymous electronic cash also known as 'blinded money' works like real hard cash. There is no trace of how the money was spent and there will be no trail of the transactions involved in this type of electronic cash. The key difference between identified electronic cash and anonymous electronic cash is that in case of identified electronic cash, bank creates the serial number, but in case of anonymous electronic cash the customer is the one who create the serial number using a blind signature process [5]. This mean that the issuing bank cannot connect the customer with the serial number of the deposited coins and, in this respect, the customer's transactions remain private [6]. As shown in Figure 2 the steps involved in anonymous electronic cash are as follows,
匿名电子现金也被称为“盲钱”,其工作原理与真正的硬现金类似。没有关于这笔钱是如何使用的痕迹,也不会有这种电子现金交易的痕迹。识别电子现金和匿名电子现金之间的关键区别在于,在识别电子现金的情况下,银行创建序列号,但在匿名电子现金的情况下,客户是使用盲签名过程创建序列号的人[5]。这意味着发行银行无法将客户与存放硬币的序列号联系起来,在这方面,客户的交易仍然是私人的[6]。如图2所示,匿名电子现金涉及的步骤如下:,
The customer will generate a random number called PQP1. From that he creates another number called blind number. Suppose the blind number is BABC.
客户将生成一个名为PQP1的随机数。由此,他创造了另一个数字,称为盲数。假设盲数为BABC。
The customer will send the created blind number to the bank. 客户将向银行发送创建的盲号。
The bank will send back the electronic cash with the blind number to the customer. 银行会将带有盲号的电子现金返还给客户。
During a transaction the customer will not use the blind number. Instead he will use the original number. 在交易过程中,客户不会使用盲号。相反,他将使用原始号码。
Therefore both the merchant and the bank will only have the original number. They cannot trace the money as they are not aware about the relationship between the blind number and the original number.
因此,商户和银行都将只拥有原始号码。他们无法追踪这些钱,因为他们不知道盲号和原始号之间的关系。
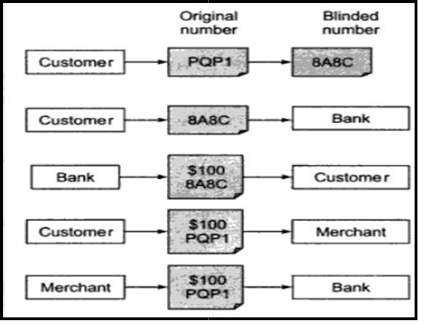
Figure 2: Steps involved in anonymous electronic cash [5]. 匿名电子现金涉及的步骤
The second method which the electronic cash can be classified is based on the involvement of the bank in transactions. Based on extend of the involvement it can be further classified as online or as offline electronic cash. When it comes to online electronic cash, the bank should actively participate in the transaction between the customer and the merchant. Such as before the purchase transaction of a specific customer get complete the merchant can verify from the bank on real time, whether the electronic cash offered by the customer is acceptable and it has not been spent before or the serial number is valid [5]. Offline electronic cash does not require an involvement of the bank to complete the transaction between the customer and merchant. If the customer offers electronic cash to a merchant, to pay for a purchase the merchant will accept the money and will not validate it online. The merchant might collect all the electronic cash and validate them together at a fixed time of everyday [5]. Hence out of these distinct types of electronic cash, it can be seen that there could be four possibilities of electronic cash. They are identified online, identified offline, anonymous online and anonymous offline electronic cash. Out of these four types, anonymous offline electronic cash creates the most complex type of electronic cash because of the double spending problem [5].
第二种电子现金分类方法是基于银行参与交易的情况。根据参与范围的扩大,可以进一步将其分为在线或离线电子现金。在网上电子现金方面,银行应积极参与客户与商户之间的交易。如在特定客户的采购交易完成前,商户可以实时从银行核实客户提供的电子现金是否可以接受,之前没有使用过,或者序列号有效。离线电子现金不需要银行参与完成客户与商户之间的交易。如果客户向商户提供电子现金,则商户将接受该笔款项,并且不会在网上验证。商户可以收集所有电子现金,并在每天的固定时间验证它们。因此,在这些不同类型的电子现金中,可以看到电子现金有四种可能性。他们在网上被识别,离线识别,匿名在线和匿名离线电子现金。在这四种类型中,匿名离线电子现金由于双重支出问题而产生了最复杂的电子现金类型。
Where as if the same piece of money is spent twice at two different places it cannot be tracked or prevented as the bank is not involved at any level of the transaction. Risk of double spending is consisted in other types of electronic cash as well. But upon detection such situations can be easily tracked and prevented as the bank is a part of the transaction at some point between customer and the merchant.
如果同一块钱在两个不同的地方花费了两次,那么就无法跟踪或阻止,因为银行不参与任何级别的交易。双倍支出的风险也包括其他类型的电子现金。但是一旦发现这种情况,就可以很容易地跟踪和防止,因为银行在客户和商户之间的某个时刻是交易的一部分。
5. Some of the Electronic cash implementations in real world 现实世界中的一些电子现金实现
Out of the electronic cash implementations DigiCash and Mondex are known as the most famous implementations of electronic cash. These two systems are similar in what they trying to achieve but different in the means of how they achieve it.
在电子现金实现中,DigiCash和Mondex被称为最著名的电子现金实现。这两个系统在他们试图实现的东西上是相似的,但在实现这两个系统的方法上却有所不同。
5.1 DigiCash DigiCash
DigiCash was founded by David Chaum in 1994. DigiCash allowed cash to be transmitted as electronic signals. The advantage of this system was that it can be used directly from the computer and did not require any additional hardware. DigiCash system used digital signature for encryption and "blind" signature for authentication to ensure the security of transactions and to protect consumers, merchants and banks from illegal activities [4]. The figure 3 given below indicated the steps involved in the process of DigiCash.
迪吉卡什是由DavidChaum于1994年创立的。DigiCash允许现金作为电子信号传输。该系统的优点是它可以直接从计算机上使用,不需要任何额外的硬件。DigiCash系统使用数字签名进行加密,并使用“盲”签名进行认证,以确保交易的安全,并保护消费者、商户和银行免受非法活动的侵害[4]。下图3显示了DigiCash过程中涉及的步骤。
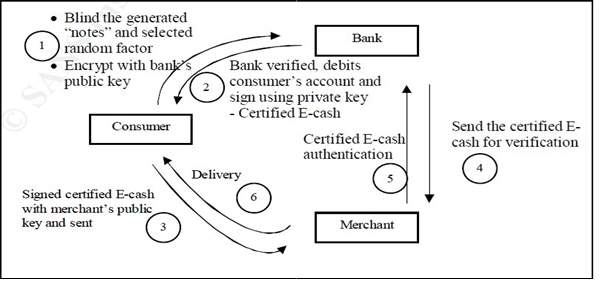
Figure: 3 Visualization of the process DigiCash [4]. 过程可视化DigiCash
DigiCash utilized a digital currency called "cyberbucks"[7]. It offered both anonymity and identified for both of its online and offline services and it allowed transfers from consumers-to-consumer in addition to consumer-tomerchant [4]. The biggest drawback of this system was, since the necessary data and electronic cash saved in the user's computer, and if the user formatted the computer's hard drive, then the user would lose his electronic cash as well. Even though DigiCash has the potential to revolutionize the monetary industry, it was failed to gain support from relevant authorities. This lead to the downfall of the system and the company.
DigiCash使用了一种名为“赛博雄鹿”的数字货币。它为其在线和离线服务提供匿名和身份认证,并允许从消费者到消费者以及从消费者到医疗中心的转移。这种系统最大的缺点是,由于必要的数据和电子现金保存在用户的计算机中,如果用户格式化了计算机的硬盘驱动器,那么用户也会丢失他的电子现金。尽管DigiCash有可能彻底改变货币行业,但它未能获得相关部门的支持。这导致了系统和公司的崩溃。
5.2 Mondex
The development of the concept for Mondex was initiated in the early 1990s.Its an E cash application based on smart cards where as electronic cash is stored in the chip located in the smart card [4]. The design of Mondex smart card allows users to transfer any amount of money electronically to the card and utilize the card to make purchases up to the value held in the card. Also Mondex accommodate card-to-card transfers as well. Mondex does not need third party to settle and clear the transactions between users. Hence it provided the advantage of speeding up the transaction. Mondex is recognized as the most secured E-cash application available as at today [4]. It has security which is based on digital signature where each message transferred between bank customer and merchant can be authenticated and it also protects consumer privacy by using blind signature. Mondex also declares that it has the ability to handle micropayments as small as one cent. The banks that currently support the Mondex smart card include National Bank of Canada, Scotiabank, Canada Trust, Bank of Montreal, Le Mouvement des caisses Desjardins, and Toronto Dominion Bank [8]. Presently, Mondex can be operated via the telephone network. In conjunction with British Telecom, the Swindon pilot allows users to load value onto their Mondex chip card using the public telephone network [6].
Mondex概念的开发始于20世纪90年代初。它是一款基于智能卡的电子现金应用程序,电子现金存储在智能卡的芯片中。Mondex智能卡的设计允许用户以电子方式将任何金额的钱转移到卡上,并利用卡进行购买,直至达到卡中持有的价值。此外,Mondex还支持卡到卡的转账。Mondex不需要第三方来结算和清算用户之间的交易。因此,它提供了加快交易的优势。Mondex是目前公认的最安全的电子现金应用程序。它具有基于数字签名的安全性,银行客户和商户之间传输的每条消息都可以通过身份验证,并且它还使用盲签名保护消费者隐私。Mondex还宣布,它有能力处理小到1美分的小额支付。目前支持Mondex智能卡的银行包括加拿大国家银行、加拿大丰业银行、加拿大信托银行、蒙特利尔银行、Le Mouvement des caisses Desjardins和多伦多自治领银行。目前,Mondex可以通过电话网络进行操作。与英国电信合作,Swindon pilot允许用户使用公共电话网络将价值加载到他们的Mondex芯片卡上。
6. Risks and issues associated with electronic cash 与电子现金有关的风险和问题
Despite of the great benefits associated with electronic cash, there are few problems caused by electronic cash towards the economy. One of the key problems identified is the taxation and money laundering [9]. Since electronic cash allows transactions across globe without any barriers taxation and money laundering has become potential problems. As for example if an Australian software provider use the American server to sell his software to a Chinese buyer ,it become questionable as if which sales tax rate should be applicable, to whom it should be applied to and whom should benefited from taxation. Since some of the electronic cash are untraceable and not leaving enough information for tax authorities to follow, it will make taxation more complicated and the adjustments toward tax regulations useless. On the other hand the untraceability ability of the electronic cash will encourage criminal activities such as money laundering .Electronic cash can also be used to deal with transactions of illegal products such as drugs, weapons and pornography. Even if the investigators wanted to conquer any evidence they will have to check for all the packets around the world and crack all cryptographies which is merely impossible. Electronic cash will potentially increase instabilities in exchange rates [9].The exchange rates in the real world and the cyber space could not be equal due to several reasons. One is, the fee of exchanging electronic currency in cyber space is lower than fee of exchanging currencies in real world as in real world the banks and financial institutions that perform currency exchange operations will have to incur additional costs such as storing bills in various currencies, managing branches and hiring workers. Electronic cash will eliminate most of these costs hence the exchange fee for electronic cash will be very low and this will encourage people for greater participation in the foreign exchange market using electronic cash. The massive participation may cause instability of exchange rates. Secondly, users of electronic cash will broaden their transaction geographically. Hence they will buy and store different varieties of electronic currencies in their hard disk to support their purchases. In the real world consumers will most likely have one currency in their hand, most probably the currency of the country or the state which they belong to. Therefore at the time of currency depreciation the consumers of electronic cash will have an incentive for speculation where as they will exchange the depreciated currency into a strong and less volatile currency in order to perform transactions. A great proportion of speculation will also lead to destabilization of the exchange rate as well.
尽管电子现金具有巨大的好处,但电子现金对经济造成的问题很少。确定的一个关键问题是税收和洗钱。由于电子现金允许全球交易,不存在任何障碍,税收和洗钱已成为潜在问题。例如,如果一家澳大利亚软件供应商使用美国服务器将其软件卖给中国买家,那么就有疑问,似乎应该适用哪种销售税率,应该适用于谁,哪些人应该从税收中受益。由于部分电子现金无法追踪,给税务机关留下足够的信息可供税务部门跟踪,这将使税收更加复杂,对税收法规的调整也就毫无用处。另一方面,电子现金的不可追踪性将鼓励洗钱等犯罪活动,电子现金也可用于处理毒品、武器和色情制品等非法产品的交易。即使调查人员想征服任何证据,他们也必须检查世界各地的所有数据包,破解所有的密码,而这些密码只是不可能的。电子现金可能会增加汇率的不稳定性。现实世界和网络空间的汇率由于几个原因无法平等。一是,网络空间中电子货币兑换费用低于现实世界的货币兑换费用,如在现实世界,执行货币兑换业务的银行和金融机构将不得不承担其他费用,例如以各种货币储存票据、管理分支机构和雇用工人。电子现金将消除大部分费用,因此电子现金的兑换费用将非常低,这将鼓励人们更多地使用电子现金参与外汇市场。大规模参与可能导致汇率不稳定。其次,电子现金的用户将在地理上扩大交易范围。因此,他们将购买和存储不同种类的电子货币在他们的硬盘支持他们的购买。在现实世界中,消费者最可能手中有一种货币,最可能是本国或所属国家的货币。因此,在货币贬值时,电子现金的消费者将有动机猜测,因为他们将贬值货币兑换成一种强大而不易波动的货币,以便进行交易。大量投机也会导致汇率的不稳定。
Furthermore electronic cash will affect the money supply in the real world [9]. Consumers of electronic cash will deposit real cash in a bank or in a financial institution and request electronic cash in exchange of the real money. If by any chance the bank or the provider of the electronic cash provide loans or lend money in the form of electronic cash, then new money will be created. On the other hand the value of electronic cash will exceed the total deposited real money. The creation of extra money could even lead to a financial crisis.
此外,电子现金将影响现实世界的货币供应。电子现金的消费者将实际现金存入银行或金融机构,并要求以电子现金兑换实际货币。如果银行或电子现金提供者以电子现金的形式提供贷款或贷款,则将创造新的资金。另一方面,电子现金的价值将超过实际存款总额。创造额外的资金甚至可能导致金融危机。
Another issue that the users of the electronic cash will have to face is the risk of asymmetric information [3]. A situation where as one party in the contract will possess more information about the object of the contract than the other party and there is a risk that the well informed party can misuse their position. In the case of electronic cash, between issuer and user, user of the electronic cash can assess the issuer only through the information published by the issuer. Yet, the issuer might face situations and circumstances which are out of the published information. Such as problems in the technology used to produce the electronic cash, not having required level of expertise, legal issues in conducting such businesses and misuse of funds which can be disadvantageous to users which will prevent users from using electronic cash.
电子现金使用者必须面对的另一个问题是信息不对称的风险。合同一方对合同标的信息比另一方拥有更多信息,知情方可能滥用其职务的风险。电子现金的发行人与用户之间,电子现金使用者只能通过发行人公布的信息对发行人进行评估。然而,发行人可能面临着信息披露之外的情况和情况。例如用于生产电子现金的技术存在问题、不需要专业知识、开展此类业务的法律问题和滥用资金,这些都可能对用户不利,从而妨碍用户使用电子现金。
7. Challenges ahead for electronic cash 电子现金面临的挑战
The biggest challenge electronic cash face as at today is that paper money still rule in retail transactions and are extensively used by small and medium sized firms. Therefore despite of the early success electronic cash has still become unable to mark its victory over the paper cash and exhibits a low level of penetration. Several factors could impact on the slow penetration of the electronic cash in to the economy. They are, consumers will like to hold on to paper money because people are more familiar with usual cash transactions as it can be carried anytime anywhere and they do not require additional electronic devices as for electronic cash. Cash can be easily withdrawn from any ATM at any time of the day. On the other hand cash transactions are also untraceable which satisfies the customer demand for privacy. In Europe, paper money may account for 76-86 per cent of retail transactions in volume, compared with 75 per cent in the USA and 90 per cent in Japan [2]. Paper money is widely used in other countries as well typically for transactions with smaller value. As for a survey conducted by Visa in 1997, taking 29 countries into consideration verified that cash transactions represented an annual value of 8.1 trillion Euros of which 22 percent was for transactions with a value of 10 Euros or less [2]. If electronic cash is making major inroads into the payment world then that evolution of volume could be visible as a rise in the share of the GDP. Yet a recent study conducted by Bank of International settlements suggest that share of coins and notes in GDP remained relatively stable in most of the OECD countries and it has only increased in the three largest OECD economies which are USA, Japan and Germany [2].
电子现金面临的最大挑战是,纸币仍然在零售交易中占据主导地位,并被中小企业广泛使用。因此,尽管电子现金早日成功,但仍无法标志着它战胜纸质现金,并显示出较低的渗透水平。有几个因素可能影响电子现金缓慢进入经济。他们是这样,消费者会喜欢持有纸币,因为人们更熟悉通常的现金交易,因为它可以随时随地携带,他们不需要额外的电子设备,如电子现金。现金可以在一天的任何时候从任何ATM机上轻松提取。另一方面,现金交易也无法跟踪,满足客户对隐私的需求。在欧洲,纸币可能占零售额的76-86%,而美国为75%,日本为90%。纸币在其他国家被广泛使用,通常用于价值较小的交易。至于Visa国际组织1997年进行的一项调查,考虑到29个国家,核实了现金交易每年价值8.1万亿欧元,其中22%用于价值10欧元或以下的交易。如果电子现金正在向支付世界大输入,那么,随着国内生产总值份额的增加,数量的演变就可以看到。然而,国际清算银行最近进行的一项研究表明,在经合组织大多数国家,硬币和纸币在GDP中的份额仍然相对稳定,而且只有在美国、日本和德国这三个经合组织最大经济体中,货币和纸币的份额才有所增加。
Another challenge that will delay the adoption of electronic cash in to the system of transactions is the startup cost. The initial cost of investment and the cost of installation will be really high with regard to the electronic cash system which will have to be passed on to the customer as a transaction fee which will cause customer to get away from these new innovations. This factor will stand out as a resistant for new entrants as it will be difficult for them to overcome the cost advantage. At the same time the speed of the technology changes and the uncertainties about these innovations discourage investors to invest in new systems.
另一个将延迟电子现金进入交易系统的挑战是启动成本。对于电子现金系统,初始投资成本和安装成本将非常高,电子现金系统必须作为交易费用转嫁给客户,这将导致客户摆脱这些新的创新。这一因素将突出对新进入者的抵抗力,因为他们很难克服成本优势。与此同时,技术变化的速度和这些创新的不确定性阻碍了投资者投资新系统。
Foot dragging by financial intermediaries such as banks is another challenge that electronic cash will face ahead. Where as in USA, consumers, businesses and the government generated nearly 650 billion paper money payments with a total value of $22 trillion. The intermediaries that handled these payments received about $190 billion in revenue, 53 per cent of which (about $100 billion) accrued to banks [2]. If a paperless cash society become a reality banks will lose all these profits and enduring benefits. Therefore the sole strategy of intermediaries is to resist and delay the adoption of electronic cash transaction systems which often have lower profit margins compared to the paper based operations.
银行等金融中介机构拖累是电子现金将面临的另一个挑战。在美国,消费者、企业和政府产生了近6500亿美元的纸币支付,总额达22万亿美元。处理这些付款的中介机构获得了大约1900亿美元的收入,其中53%的收入(约1000亿美元)应计给银行。如果一个无纸现金社会成为现实,银行将失去所有这些利润和持久的利益。因此,中间商的唯一策略是抵制和推迟采用电子现金交易系统,这些系统通常比纸质业务利润率低。
8. Recommendations 建议
In order face the challenges ahead and to avoid or to mitigate the impact of the prevailing risks, adequate regulatory, technical and protection measurements should be taken into considerations. Such as effective supervision on issuers of electronic cash and clearly defined and disclosed solid, transparent legal agreements indicating the rights and obligations of respective participant in the scheme of electronic cash should be enforceable under all jurisdictions. Laws and regulations should be drafted to protect users against criminal abuses such as money laundering. On the other hand merchants such as restaurants, supermarkets and hotels should be stimulated to accept electronic cash by giving them additional advantages. Furthermore enhancing the infrastructures to deal with electronic cash such as ATMs and providing adequate publicity and educating the participants about the electronic cash and the privileges to holders will help the electronic cash scheme to overcome the challenge of low penetration of electronic cash.
为了应对未来的挑战,避免或减轻当前风险的影响,应考虑采取适当的监管、技术和保护措施。例如,对电子现金发行人的有效监管,以及明确定义和披露的坚实、透明的法律协议,表明电子现金计划各参与者的权利和义务,应在所有司法管辖区内强制执行。应起草法律和法规,保护用户免受洗钱等犯罪行为的侵害。另一方面,餐馆、超市和酒店等商家应该通过提供额外优势来鼓励他们接受电子现金。此外,加强处理电子现金(如ATM)的基础设施,并向参与者提供有关电子现金和持有人特权的充分宣传和教育,将有助于电子现金计划克服电子现金渗透率低的挑战。
9. Conclusion 结论
Along with significant development and progresses made, electronic cash has begin to play an important role among the key segments of the economy such as payment systems, retail transactions and international trading. The digital signature and blind digital signature play an important role in implementing the electronic cash. It has enhanced the security and privacy of electronic cash which tempt users to select electronic cash over traditional paper money. Even though the market share of paper money is yet to be more than the electronic cash in most of the countries it is gradually increasing among the countries with large economies. Likewise with the introduction of new electronic cash instruments will provide a broader acceptance for electronic cash for a range of transactions into the future. Hence it is required for such instruments to overcome the strong obstacles which curtail the fast penetration of electronic cash into the economy. At the same time it is mandatory to have appropriate regulatory and institutional systems in place to handle the economic forces which are at play as consequence of electronic cash. With these factors been taken into consideration, electronic cash will have the potential to acquire larger segment of the payment and transaction market into the future and even to totally replace paper money lead the world toward an networked economic environment.
References 参考文献
[1]"REPORT ON ELECTRONIC CASH", European Central Bank, Frankfurt, 1998.
[2] M. Andrieu, "The future of e‐money: main trends and driving forces", Foresight, vol. 3, no. 5, pp. 429-451, 2001. Available:
10.1108/14636680110416779.
[3] S. Bećirović, "CHALLENGES FACING E-MONEY", University journal of Information Technology and Economics, vol. 1, no. 2335-0628, 2014.
[4]Giac.org,2019.
[5] A. kahate, cryptography and network security, 2nd ed. New Delhi: Tata McGraw- Hill Publishing company limited, 2008.
[6] L. Srivastava and P. Mansell, "Electronic Cash and the Innovation Process: A User Paradigm", Science Policy Research Unit, University of Sussex, Brighton, 1998.
[7]"DigiCash", Investopedia,2019.
com/terms/d/digicash.asp. [Accessed: 30- Oct- 2019].
[8]"Mondex Smart Card", Tech-faq.com, 2019.
[9]T.Tanaka,"Possible economic consequences of digital
cash", Firstmonday.org,2019.
[10] G. Papadopoulos, "Electronic Money and the Possibility of a Cashless Society", SSRN Electronic Journal, 2007. Available: 10.2139/ssrn.982781.
Banking Essay写作格式范文在最后的总结部分中提到随着电子现金的显著发展和进步,电子现金已开始在支付系统、零售交易和国际贸易等关键经济领域发挥重要作用。数字签名和盲数字签名在电子现金的实现中起着重要的作用。它增强了电子现金的安全性和隐私性,吸引用户选择电子现金而不是传统的纸币。尽管在大多数国家,纸币的市场份额尚未超过电子现金,但在经济大国中,纸币的市场份额正在逐渐增加。同样,随着新电子现金工具的引入,电子现金将在未来的一系列交易中得到更广泛的接受。因此,Essay写作格式范文总结这类工具需要克服阻碍电子现金快速渗透到经济中的强大障碍。同时,必须建立适当的监管和制度体系,以应对电子现金带来的经济力量。考虑到这些因素,电子现金将有可能在未来获得支付和交易市场的更大份额,甚至完全取代纸币,引领世界走向网络化经济环境。本站提供各国各专业Essay写作指导服务,如有需要可咨询本平台。
